CNC machine tools are like turbochargers for modern manufacturing, bringing us unprecedented levels of precision and efficiency. With these mechanical marvels, we can now tackle complex tasks that were once impossible to complete by hand. Picture this: skilled craftsmen operating CNC machines are reshaping the metal world with code and precision tools, constantly driving technology forward. Whether we’re seasoned machinists, curious tech enthusiasts, or business owners, understanding the various types of CNC machines helps us appreciate their core role in today’s industrial world.
In this realm of metal and machinery, six types of CNC machines stand out. First, CNC milling machines are dedicated to cutting complex shapes, while CNC lathes bring perfect symmetry to cylindrical pieces. For detailed carving on wood and plastic, CNC routers excel with their fine and delicate work. Meanwhile, plasma cutters and laser cutters combine speed and precision in metal cutting, and EDM machines are essential tools for processing hard metals, particularly in mold-making.
In this article, we’ll explore these six common types of CNC machines, each with its own unique functions and uses, showcasing the strength and spirit of modern manufacturing.
1. What is a CNC Machine?
A CNC machine (Computer Numerical Control machine) is an automated machining tool controlled by a computer. Unlike traditional machines that require manual operation, CNC machines rely on computer programs to precisely control the position, speed, angle, and other parameters of the cutting tools. This allows them to perform tasks like cutting, milling, drilling, and turning on various metal workpieces. With computer control, CNC machines can achieve levels of precision and complexity that are hard to reach with manual methods, making them widely used in modern manufacturing.
2. Six Common Types of CNC Machines
CNC Milling Machine
A CNC milling machine is a piece of equipment that uses a computer numerical control system to handle milling tasks. It has a rotating cutting tool that moves along a programmed path, allowing it to cut, carve, and shape materials. CNC milling machines work well with metals, plastics, wood, and composites, offering high-precision 3D machining to create complex parts and shapes.
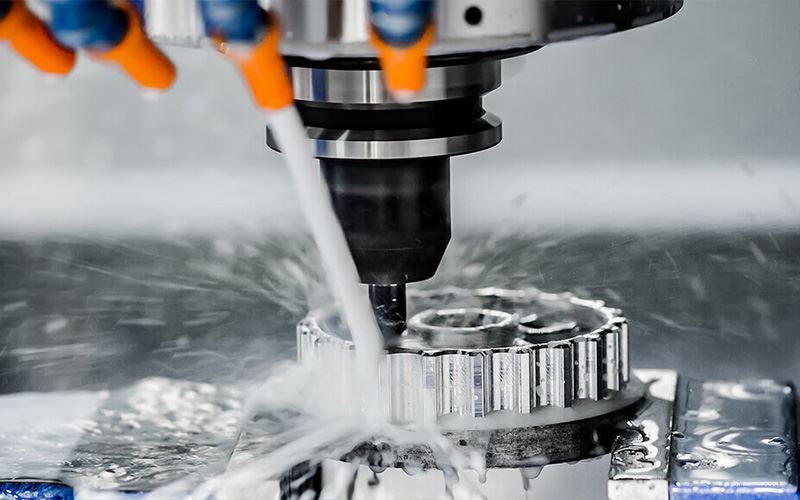

How a CNC Milling Machine Works
At the heart of a CNC milling machine is the computer control system. The operator inputs the machining path and parameters through a programming language, such as G-code. The computer then precisely controls the movement and rotation speed of the cutting tool based on these instructions. During the process, the workpiece is securely held on the worktable while the cutting tool moves around it, removing material and forming the desired shape.
Key Features of CNC Milling Machines
- Multi-Axis Control: CNC milling machines typically have 3, 4, or even 5 axes, allowing the cutting tool to move in various directions for complex 3D machining. With 5-axis machines, the tool can cut the workpiece from multiple angles, making it suitable for parts with intricate geometries.
- Automation: CNC milling machines are highly automated, capable of continuously machining various parts with minimal manual intervention, thus boosting production efficiency.
- High Precision: Thanks to the numerical control system, CNC milling machines achieve extremely high precision, ensuring better consistency and minimal errors in part production.
Applications of CNC Milling Machines
CNC milling machines find extensive use across many industries:
- Automotive Industry: They are essential for manufacturing precision parts like engine components, gearboxes, and steering systems.
- Aerospace: These machines produce aircraft components such as wings and turbine blades, where high accuracy is crucial.
- Medical Equipment: CNC milling machines manufacture surgical tools, implants, and other precision medical devices.
- Mold Making: They are used to create various types of molds, including plastic molds, die-cast molds, and injection molds.
CNC Lathes
A lathe is a machine tool that rotates a workpiece while a cutting tool moves along a specific path to shape it. The lathe is one of the oldest and most fundamental machine tools, used to produce cylindrical objects like shafts, threads, and casings. Even today, it remains essential in modern manufacturing and is widely used in industries like automotive manufacturing, machining, and aerospace equipment production.
Working Principle of the Lathe
The lathe operates on the principle of rotational cutting. During operation, the workpiece is secured to the main spindle and rotates at high speed, while the cutting tool follows a preset path to cut the surface. This method removes material to form a specific shape. Operators can adjust the rotation speed, feed rate, and cutting depth according to the needs of the job, achieving the desired surface quality and dimensions.
Main Types of Lathes
There are many types of lathes, each suited for different machining needs:
- Conventional Lathes: These are good for machining simple cylindrical parts and have basic functions, making them suitable for small-scale production.
- CNC Lathes: Equipped with computer numerical control systems, these lathes automate the machining process and are ideal for batch production of precision parts. CNC lathes have an advantage over conventional lathes in terms of speed and consistency.
- Automatic Lathes: These are perfect for high-volume production, capable of performing multiple machining steps in one cycle, usually for small parts.
- Vertical Lathes: Here, the workpiece is mounted vertically, making them suitable for machining large, heavy parts like wheel hubs and large flanges.
Main Applications of Lathes
Thanks to their versatility, lathes are widely used in many industries:
- Automotive Industry: They are used to produce cylindrical parts like steering shafts, wheel hubs, and transmission shafts.
- Aerospace: They are employed for machining aircraft components, especially symmetric parts.
- Machinery Manufacturing: They are useful for producing various shafts, casings, and rotating components.
- Metalworking: Lathes handle threading, surface polishing, drilling, and turning, among other tasks.
Advantages of Lathes
- High Precision: By precisely controlling the workpiece’s rotation speed and the cutting tool’s feed rate, lathes produce high-precision cylindrical parts.
- Versatility: Lathes perform multiple operations, such as cutting, drilling, polishing, and threading, covering a wide range of applications.
- High Efficiency: Modern CNC lathes complete complex parts quickly, making them ideal for large-scale production.
CNC Routers
A CNC Router is a computer-controlled engraving machine used for cutting, engraving, and drilling materials. This machine typically works with lighter materials, such as wood, plastic, foam board, and even soft metals. Known for its high precision and flexibility, the CNC router can create intricate patterns and fine details, making it popular in furniture manufacturing, sign making, and model carving.
Working Principle of CNC Routers
The working principle of a CNC router is similar to that of a CNC milling machine. It uses a rotating tool, or engraving bit, to cut and carve materials fixed onto the worktable. The operator inputs the desired machining path through computer programming, allowing the machine to adjust the tool’s movement automatically according to these paths. This ensures accurate engraving of various patterns and shapes. CNC routers often feature multi-axis systems, such as three-axis or four-axis configurations, enabling the tool to process the material from multiple angles.
Key Features of CNC Routers
- High Precision: CNC routers precisely control tool positioning and depth, resulting in beautiful and consistent engraving.
- Versatility: These machines handle multiple processes like cutting, engraving, drilling, and boring, making them suitable for different materials and tasks.
- High Automation: The entire engraving process runs under computer control, minimizing manual intervention and boosting productivity.
- Supports Various Materials: Though mainly used with lighter materials, some high-power CNC routers can also process soft metals like aluminum.
Main Applications of CNC Routers
Thanks to their versatility, CNC routers find use in many industries:
- Furniture Manufacturing: They engrave patterns, designs, and decorative details on furniture, enhancing aesthetics.
- Sign Making: CNC routers carve out signs, logos, and letters, quickly producing company logos and intricate text for advertising.
- Craft Design: These machines create exquisite wood carvings, reliefs, and decorative items, making them ideal for small-scale craft production.
- Model Making: They assist in creating architectural models, product prototypes, and toys, completing complex shapes and details in a short time.
Advantages of CNC Routers
- High Precision: CNC routers deliver exact detail work, which is especially suitable for artistic designs and decorations.
- Simple Operation: Computer control manages the entire engraving process, requiring only programming to start, thus reducing manual operation complexity.
- High Efficiency: Multi-axis routing systems can process several surfaces at once, significantly reducing work time.
- Batch Production Support: CNC routers allow for simultaneous machining of multiple identical parts, making them suitable for large-scale production.
CNC Plasma Cutters
A CNC Plasma Cutter is a high-efficiency metal cutting machine controlled by a computer numerical control (CNC) system. Using a plasma arc, it rapidly heats and cuts conductive metals, including steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and copper. With its fast cutting speed, high cutting quality, and versatility in material compatibility, the CNC plasma cutter is widely used in manufacturing, metal processing, and construction industries.

Working Principle of CNC Plasma Cutters
The core principle of a CNC plasma cutter is plasma arc cutting. During cutting, gas—such as compressed air, oxygen, or nitrogen—passes through an electric arc, ionizing and forming a high-temperature plasma arc that can reach up to 30,000 degrees Celsius. This plasma arc heats the metal to its melting point, while a high-pressure gas flow quickly blows away the molten metal, creating a clean cut. The CNC system precisely controls the plasma cutting head’s path, speed, and height to ensure both cutting quality and efficiency.
Key Features of CNC Plasma Cutters
- High Cutting Speed: Plasma cutting is much faster than traditional cutting methods, especially for thick metal sheets.
- Precision Cutting: The high temperature of the plasma arc and accurate control result in smooth, neat cut edges, reducing the need for post-processing.
- Multi-Material Compatibility: CNC plasma cutters handle various conductive metals and accommodate different sheet thicknesses.
- Cost-Effective: Compared to laser cutters, plasma cutters have lower equipment and maintenance costs, making them ideal for batch production and fast-cutting tasks.
Main Types of CNC Plasma Cutters
Based on cutting methods and applications, CNC plasma cutters include:
- Air Plasma Cutters: These use compressed air for cutting, suitable for light-duty cutting tasks.
- High-Frequency Plasma Cutters: With high-frequency power supplies and different gases, these provide enhanced cutting precision.
- Underwater Plasma Cutters: These cutters operate underwater to reduce smoke and noise, ideal for thick metal sheets.
- Portable Plasma Cutters: Compact and mobile, these are perfect for on-site work or small workshops.
Main Applications of CNC Plasma Cutters
Thanks to their speed and adaptability, plasma cutters are widely used in various industries:
- Manufacturing: They support large-scale production for automotive, heavy machinery, and metal structures.
- Construction: Plasma cutters handle steel, structural components, and building frameworks, suitable for on-site cutting and structural processing.
- Metal Processing: They cut metal sheets and pipes, working well with materials like steel and aluminum.
- Maintenance and Repair: Portable and fast, plasma cutters are ideal for on-site repairs of metal parts or structural components.
Advantages of CNC Plasma Cutters
- High Efficiency: With fast cutting speeds, plasma cutters excel in high-volume and high-speed cutting tasks.
- Quality Cuts: Plasma cutters produce smooth, clean cuts with minimal post-processing needed.
- Low Operating Costs: Maintenance costs are relatively low, and the machines are highly adaptable for use in different industries.
- Flexibility: They cut metal sheets of varying thicknesses and materials, offering broad application possibilities.
CNC Electrical Discharge Machines (EDM)
A CNC Electrical Discharge Machine (EDM) is a precision machine tool that uses electrical discharges to process conductive materials. With computer numerical control (CNC), it generates high-frequency electric sparks between the electrode and the workpiece, etching the material layer by layer to form the desired shape. CNC EDM machines are perfect for processing high-hardness metals and can create complex geometric shapes. Therefore, they are widely used in mold manufacturing, aerospace, and precision engineering.

Working Principle of CNC EDM
The core process of a CNC EDM involves discharge etching. During machining, a narrow gap forms between the tool electrode and the workpiece, and electric sparks within this gap instantly generate temperatures high enough (several thousand degrees Celsius) to melt or even vaporize the material. As the electrode slowly approaches the workpiece, each discharge removes tiny amounts of material, gradually forming the desired shape. The CNC system precisely controls the entire process, achieving high-accuracy machining.
Main Types of CNC EDM
CNC EDM machines come in various types based on different processing methods:
- Sinker EDM: This type uses custom electrodes to discharge directly onto the workpiece, suitable for processing complex shapes, and commonly used in mold manufacturing.
- Wire EDM: Here, a metal wire serves as the electrode, moving to cut the workpiece. It’s ideal for intricate contouring and complex shapes.
- Hole Drilling EDM: This type specializes in processing small, deep holes, such as nozzle holes and cooling channels.
Key Features of CNC EDM
- High Precision: CNC EDM machines offer extremely high machining accuracy, achieving micron-level details and making them ideal for precision parts.
- Non-Contact Processing: Electrical discharge does not require physical contact with the workpiece, avoiding mechanical stress and making it suitable for brittle materials and precision machining.
- Capability for Hard Materials: EDM machines process hard metals, such as carbide and titanium alloys, with a broad range of applications.
- Complex Shape Machining: With custom electrodes and CNC control, EDM can produce complex geometries that other machines cannot handle.
Main Applications of CNC EDM
CNC EDM is widely used for high-precision and high-hardness material processing, including:
- Mold Manufacturing: EDM machines help produce complex shapes for plastic injection molds, die-casting molds, and stamping dies.
- Aerospace: They process high-strength, high-precision parts like aircraft engine components and turbine blades.
- Medical Devices: EDM machines manufacture precision medical equipment, such as implants and surgical instruments.
- Electronics Industry: They create precision connectors, terminals, and miniature parts to meet the needs for miniaturization and high precision in electronic products.
Advantages of CNC EDM
- High Precision and Complex Shapes: EDM achieves exceptionally high accuracy, making it ideal for parts with complex geometries.
- Versatility: EDM machines process nearly all conductive materials, including hard metals that are challenging for traditional cutting methods.
- No Mechanical Deformation: Since the electrode and workpiece do not touch during machining, there is no mechanical deformation or stress on the workpiece.
- No Tool Wear: The tool electrode does not directly contact the workpiece, so it experiences minimal wear, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
CNC Laser Cutting Machines
A CNC Laser Cutting Machine is a device that uses computer numerical control (CNC) and high-energy laser beams to precisely cut and engrave various materials, including metal, plastic, and wood. The machine focuses the laser on the material’s surface, causing it to heat up, melt, or vaporize instantly, thus achieving fine cutting results. Due to its high precision and versatility, CNC laser cutting machines find widespread application in manufacturing, advertising, crafts, and electronics production.
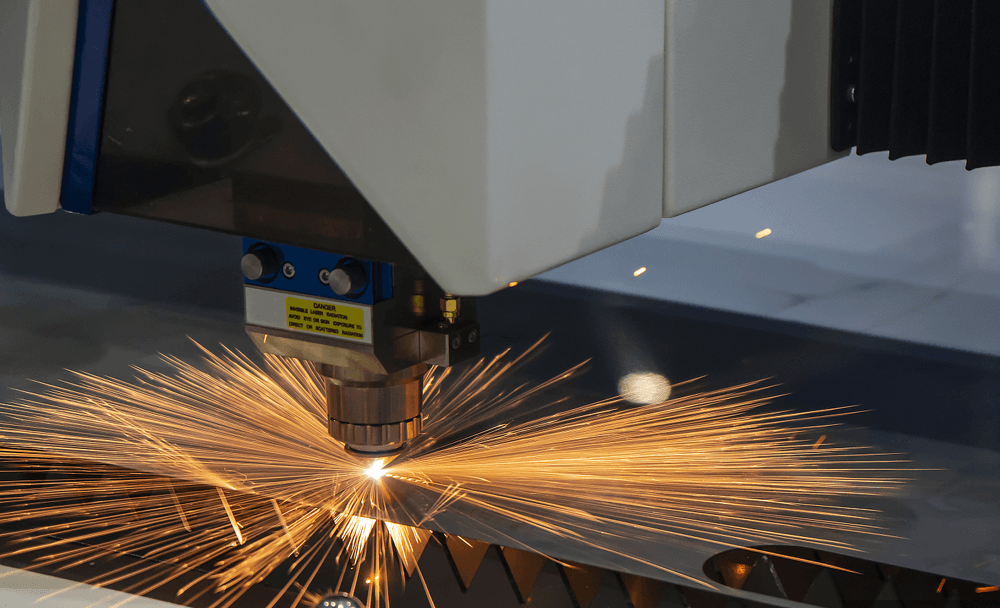
Working Principle of CNC Laser Cutting Machines
CNC laser cutting machines generate high-energy laser beams through a laser source. The machine focuses this beam onto the material’s surface, creating high temperatures. Auxiliary gases, such as oxygen or nitrogen, then blow away the molten material from the cutting area, resulting in smooth cuts. The CNC system precisely controls the laser’s movement path, power, and speed, enabling it to cut complex and intricate shapes.
Main Types of CNC Laser Cutting Machines
CNC laser cutting machines generally fall into several categories based on the type of laser source:
- CO₂ Laser Cutting Machines: These machines are suitable for non-metal materials such as wood, plastic, and fabric, with some capability for cutting thin metals.
- Fiber Laser Cutting Machines: Primarily used for cutting metal materials like stainless steel, aluminum, and copper, these machines offer fast cutting speeds and high precision.
- YAG Laser Cutting Machines: These machines are suitable for cutting thin metal sheets and are often used for industrial engraving and fine processing.
Advantages of CNC Laser Cutting Machines
- High Precision: Laser cutting machines achieve micron-level machining precision, resulting in smooth cuts that require no additional polishing.
- High Efficiency: They operate at high cutting speeds, especially for thin materials, significantly reducing production time.
- Versatility: In addition to cutting, these machines can also engrave, mark, and drill, accommodating various complex processing needs.
- Non-Contact Processing: The laser beam does not contact the material, avoiding mechanical pressure. This feature makes it ideal for processing brittle or soft materials.
Applications of CNC Laser Cutting Machines
CNC laser cutting machines are widely used across multiple industries:
- Metal Processing: They cut materials like steel, stainless steel, and aluminum, commonly used for manufacturing automotive parts and appliance casings.
- Advertising Production: These machines create signs, billboards, and plaques, enabling quick engraving of intricate designs and text.
- Craft Production: They cut and engrave materials like wood and leather, allowing for the creation of exquisite decorative items, gifts, and artworks.
- Electronics Industry: CNC laser cutting machines produce small electronic components and circuit boards, meeting the demands for precision processing.
The diversity and unique advantages of CNC cutting machines make them indispensable tools across various industries. From the high-speed precision of plasma cutters to the complex shape processing of EDM machines, each machine type brings endless possibilities to modern manufacturing. If you have further questions about the different types of CNC machines or wish to learn more about how these technologies can enhance your production, we are here to offer professional advice and support. Please visit Minnuo Group’s official website and get in touch with us. We look forward to helping you unlock the full potential of these technologies and meet your manufacturing needs more efficiently!












