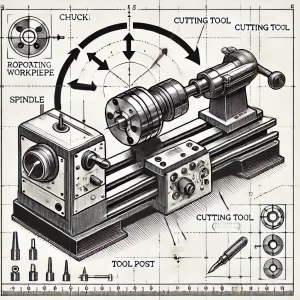
In manufacturing, the choice of machining processes is crucial for product quality, cost control, and production efficiency. Whether for precision machining or mass production, selecting the right process shapes the product’s market competitiveness. Especially for complex processes requiring high precision, choosing the most suitable machining process not only boosts product quality but also significantly reduces production costs.
There are nine core machining processes—milling, turning, grinding, drilling, broaching, wire EDM, laser cutting, injection molding, and stamping—that cover nearly all common metal and plastic machining needs. Each process offers different levels of accuracy, efficiency, and material compatibility, so selecting the right process becomes essential for effective production planning. Faced with complex tasks, companies need to consider the structural features of the product, while also balancing factors like cost, batch size, and processing time.
In the following content, we will break down these nine core machining processes. We will analyze each process’s characteristics, suitability, pros, and cons, along with specific solutions for particular needs, helping decision-makers and technical staff find the best process combinations. This will enable companies to efficiently meet production needs, control costs, and strengthen their product’s market position.
Milling: A Versatile Process for Diverse Needs
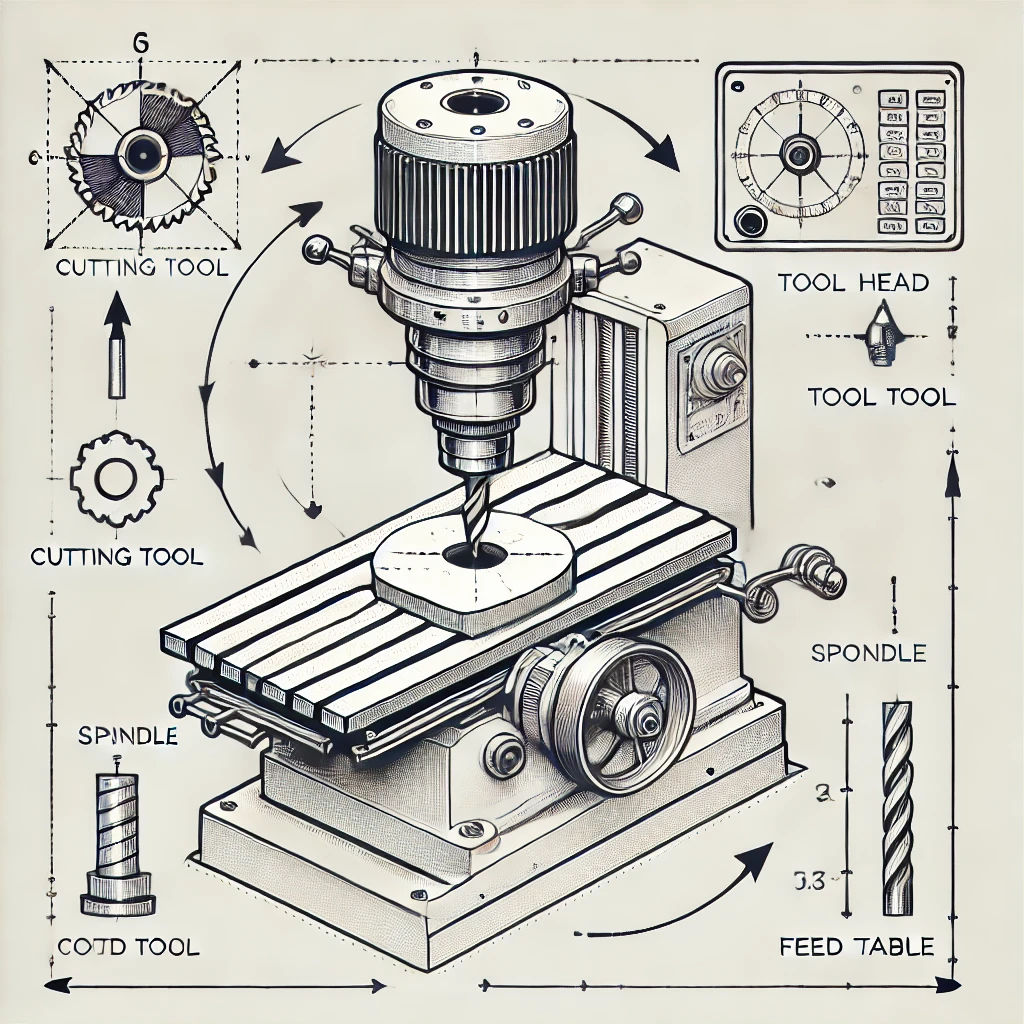
Milling can handle flat surfaces, slopes, grooves, and even complex 3D curves. With multi-directional tool rotation, milling can complete various cutting tasks on a single part, significantly boosting efficiency. Mechanical production widely uses milling for shaping, edging, and surface machining, especially for parts that require precise contours, such as molds, equipment housings, and other components.Its versatility makes it suitable for a wide range of production needs. However, when working with high-hardness materials, milling can face challenges, as cutting tools wear down quickly when handling tough, abrasive materials.
Turning: The Efficient Expert for Cylindrical Parts
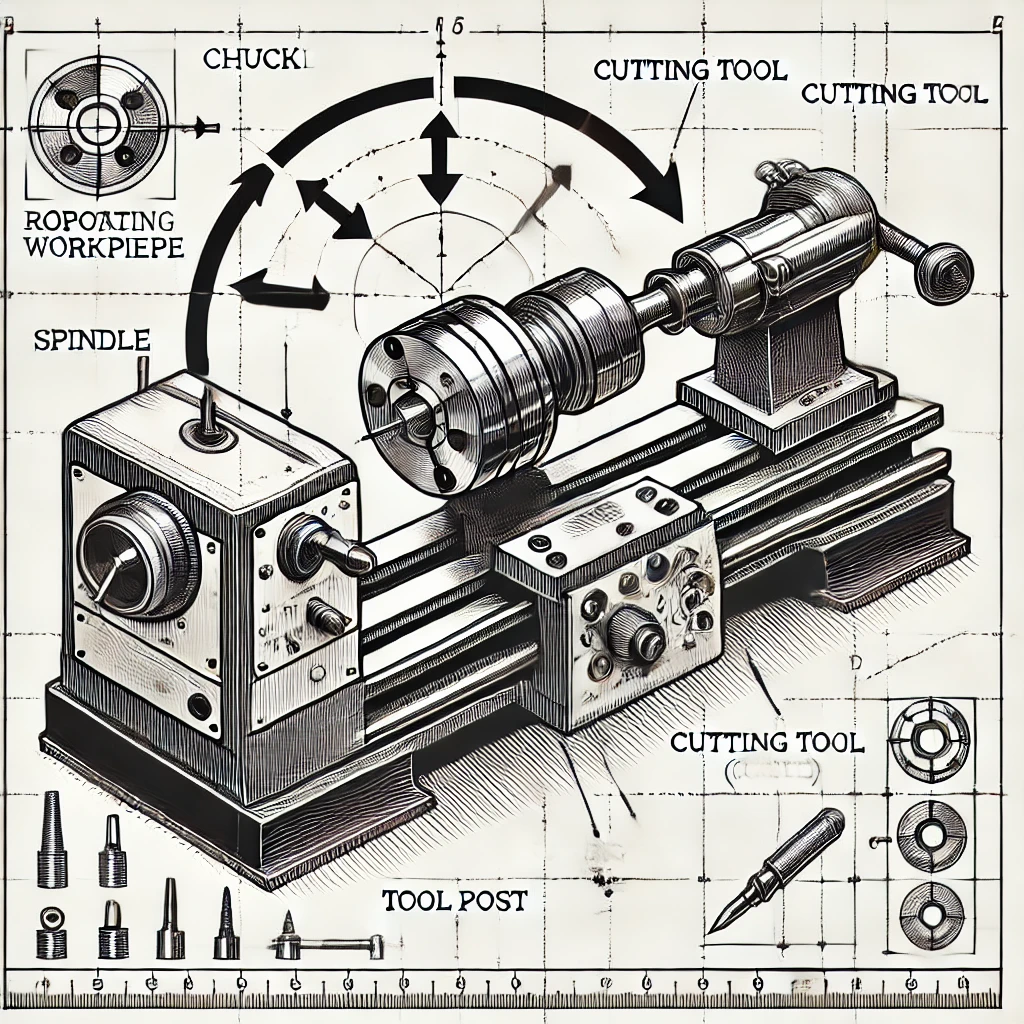
In turning, the workpiece rotates while the cutting tool shapes it, making turning ideal for cylindrical parts like shafts, sleeves, and other rotationally symmetrical items. The biggest advantage of turning lies in its speed and stability, ensuring high efficiency and smooth surface finishes. For example, it is often used on production lines for automotive drive shafts or hydraulic piston rods. Turning maintains high precision for each part and allows operators to adjust feed rate and cutting depth to control surface smoothness. However, turning is less effective for irregularly shaped parts since it relies on continuous rotation of the workpiece.
Grinding: Precision and Smooth Finishes for High Standards
Known for its high precision and ability to achieve ultra-smooth finishes, grinding is essential in fine machining. Typically, grinding serves as a final step to refine the surface of already-shaped parts, especially for applications with strict requirements for surface quality and precision, such as bearings, molds, and precision instruments. During grinding, the wheel removes minimal material, reaching micrometer-level precision and creating mirror-like surfaces. Grinding excels with hard materials like hardened steel, stainless steel, and carbides, though its higher cost usually makes it best suited for low-volume production or specialized applications.
Drilling: Simple, Fast, and Essential for Basic Machining
Drilling is one of the most common machining processes and specializes in making holes efficiently. It is suitable for both small-batch and mass production. Whether creating assembly, threaded, or positioning holes in mechanical parts, drilling is the go-to choice. It offers high efficiency, but hole quality depends heavily on the drill bit and coolant. For larger holes or high-precision requirements, follow-up finishing processes may be necessary to ensure consistent hole size and quality.
Broaching: Rapid, High-Precision Shaping for Complex Grooves
Broaching is a specialized process for creating complex slots and irregular holes in one pass. It’s exceptionally efficient, especially for producing standardized parts, like keyways and splines in the automotive and machinery industries. Although broach manufacturing and maintenance can be costly, broaching is well-suited for high-volume production. Its main advantage lies in its ability to create complex shapes with high precision and consistency in a single operation, eliminating the need for secondary processing.
Wire EDM: Precision Cutting for Complex Shapes and Hard Materials
Using electrical discharge to cut precisely, wire EDM is perfect for high-hardness and difficult-to-machine materials, making it invaluable in mold manufacturing and precision machining. Wire EDM achieves exceptional contour accuracy on metals, unaffected by material hardness, making it ideal for intricate cuts, such as small mold parts and carbide components. Though processing speed is relatively slow, wire EDM provides the micrometer-level precision needed for hard materials or irregular shapes.
Laser Cutting: High-Speed, Contactless Cutting Specialist
Laser cutting uses a high-energy beam for cutting, making it suitable for thin sheets, including both metal and non-metal materials, particularly when fast shaping is needed. Since it requires no contact with the workpiece, laser cutting achieves high accuracy without risking surface deformation. This rapid-cutting capability is ideal for thin sheets and intricate profiles, such as sheet metal, decorative items, and signage. With its high speed and flexibility, laser cutting is suitable for fast customization and small-batch production.
Injection Molding: The High-Volume Solution for Plastic Parts
Injection molding injects molten plastic into molds, cooling and shaping it efficiently, making it perfect for mass production of plastic parts. This method excels in speed and consistency, ideal for intricate plastic items that need high uniformity, such as appliance housings, consumer electronics, and automotive interior parts. Though mold development is costly, injection molding’s low per-unit cost makes it highly economical for large-scale production.
Stamping: Batch Production for Sheet Metal Components
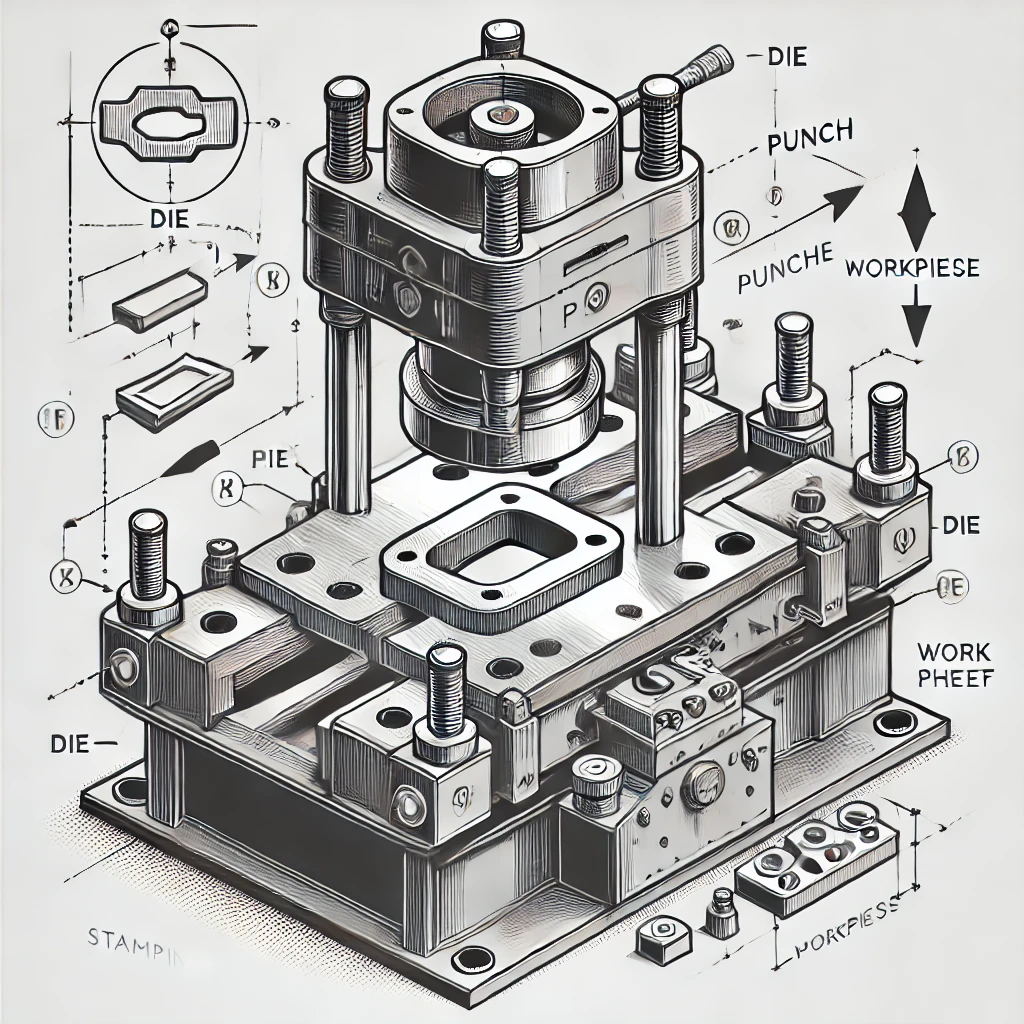
By applying pressure through molds to shape sheet metal, this process combines high efficiency with low cost, making it especially suited for batch production of metal sheets. Large-scale production with short cycle times suits stamping well, and manufacturers commonly use it for automotive exteriors, appliance panels, and other metal sheets. It maintains low per-part cost and offers long mold lifespan, making it ideal for high-volume, standardized sheet metal production.
Guide to Selecting Machining Processes: Making Smart Choices Based on Needs
In actual production, choosing the right machining process not only determines product quality and delivery efficiency but also directly affects cost control and a company’s competitiveness. The following guide examines various dimensions—such as product characteristics, materials, production volume, and budget—providing a clear and actionable approach to finding the best machining process for your needs.
Analyze Product Characteristics: Match the Process to the Product
The geometry, precision requirements, and surface finish of a product are the primary factors that determine the most suitable process. Here are some suggestions to align product needs with the right process:
- Complex 3D Shapes: For parts with detailed 3D curves, like molds and intricate structural components, wire EDM or laser cutting are recommended. These processes allow precise contouring, making them ideal for molds and other complex, high-precision items.
- Shafts and Rotational Parts: For standard shaft-like parts or other rotationally symmetric components, turning is the most efficient option. This process not only offers excellent speed but also maintains the roundness and concentricity of shaft-type parts.
- High Precision and Smooth Surfaces: For parts with strict requirements on smoothness and accuracy, like bearing housings and precision mold components, grinding is highly suitable. It achieves micron-level precision and delivers outstanding surface quality.
Consider Material Properties: Match the Process to the Material
Different materials vary significantly in hardness, ductility, and heat resistance, so it’s essential to select processes that align with these properties to achieve optimal results and extend tool life.
- High-Hardness Metals: For high-hardness materials like carbide and tool steel, grinding or wire EDM works best. These processes handle tough materials well and reduce tool wear.
- Plastics and Composites: For plastics and composites, injection molding is ideal. It produces complex parts with high consistency in a short time, making it widely used in consumer electronics and automotive industries.
- Thin Sheets and Heat-Resistant Metals: Materials like steel sheets and aluminum are best suited to laser cutting or stamping. Laser cutting offers high precision and contactless processing, while stamping is great for batch production of metal parts, especially in automotive and home appliance manufacturing.
Determine Production Volume and Cost: Adapt Processes Based on Scale
The production volume of a product has a direct impact on process selection. Choosing the right process for the batch size can greatly reduce costs and improve efficiency.
- High-Volume Production: For parts needing high-volume production, especially stable shapes with simple requirements, stamping or injection molding is ideal. Both processes reduce unit cost, feature simple operations, and support automation, making them perfect for products with long production cycles and stable demand.
- Small Batch or Custom Production: For small batches or custom production, laser cutting or milling is recommended. Laser cutting offers fast speeds and simple programming, making it suitable for intricate shapes, while milling provides flexibility to quickly produce parts of varying shapes without custom molds, reducing upfront costs.
Balance Budget Control: Find the Best Combination of Needs and Budget
The costs of different processes can vary significantly, so companies need to find the best combination that meets production requirements within their budget.
- Low Budget, Small Production Runs: When budget is limited and batch sizes are small, milling and turning are cost-effective choices. They don’t require expensive molds and are suitable for small batches and customized parts. For example, turning can efficiently and affordably achieve high precision and speed for simple metal parts.
- High Budget, Large-Scale Production: For cases with a larger budget and high production volume, prioritize stamping and injection molding. These processes suit large-scale production well, as increased volume quickly offsets higher initial mold costs by reducing unit costs.These processes suit large-scale production well, as increased volume quickly offsets higher initial mold costs by reducing unit costs.They work particularly well for high-demand products like automotive parts and household appliance components.
Why Choose Minnuo Machining Equipment
Faced with diverse machining needs, Minuo is dedicated to providing customers with cost-effective equipment across core machining processes from the nine major methods. Minuo offers highly customized solutions tailored to different production needs. Whether you need high-speed milling, precision turning, grinding, or versatile laser cutting, Minuo equipment undergoes rigorous testing and delivers key advantages:
- High Stability: Minuo equipment maintains high stability alongside precision, which reduces maintenance time and boosts production efficiency.
- Efficient Energy Management: Minuo machines feature excellent power control and integrate eco-friendly design, helping customers lower production costs while supporting sustainable practices.
- Integrated Solutions: Minuo’s comprehensive range supports multiple applications—from turning to grinding to laser cutting—offering smooth transitions between operations and increasing production flexibility.
- Excellent After-Sales Service: With a skilled technical team and extensive industry experience, Minuo provides full after-sales support along with guidance for process optimization.
Conclusion
Whether for small-scale startup production or a full-scale factory line, choosing the right machining process and a reliable equipment supplier are essential to success. By understanding the characteristics and applications of the nine major machining processes and by using Minuo’s high-quality equipment, you can streamline your production, improve efficiency, and ultimately gain a competitive edge in the market.