Are you considering adding a desktop CNC mill to your toolkit? Desktop CNC mills have revolutionized the way hobbyists, small business owners, and engineers approach manufacturing and prototyping.
Desktop CNC mills are compact, computer-controlled machines designed for milling, drilling, and cutting a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and wood. They are perfect for small-scale manufacturing, prototyping, and educational purposes, offering high precision and versatility at a lower cost compared to industrial CNC mills.
Whether you’re a seasoned machinist or a beginner looking to explore CNC technology, this guide will help you understand everything you need to know about desktop CNC mills, from their components to their applications and how they compare to other types of milling machines.
What is a Desktop CNC Mill?
A desktop CNC mill is a small, computer-controlled milling machine designed for a variety of tasks, including milling, drilling, and cutting different materials such as metals, plastics, and wood. Unlike larger industrial CNC mills, desktop models are compact and affordable, making them accessible to hobbyists and small businesses alike. These machines use software to control precise movements, allowing users to create detailed parts and prototypes with ease.
Key Components of a Desktop CNC Mill
Understanding the key components of a desktop CNC mill is crucial for maximizing its capabilities. Here’s a breakdown of the most important parts:
Frame and Structure: Usually made from materials like aluminum or steel, the frame provides stability and precision. A rigid frame reduces vibrations, ensuring accurate cuts.
Spindle: The spindle is the rotating component that holds and spins the cutting tool. Desktop CNC mills can have air-cooled or water-cooled spindles, each suitable for different types of materials and cutting speeds.
Drive System: The drive system, typically using stepper or servo motors, moves the spindle and cutting tool with high precision. Linear guides and ball screws are used for accurate movement along the X, Y, and Z axes.
Control System: The control system includes the software and electronics that direct the machine’s operations. Popular options include GRBL, Mach3, and proprietary systems that allow for user-friendly interfaces and complex programming.
Tooling and Tool Changers: Various tools, such as end mills and drill bits, are used depending on the task. Some advanced desktop CNC mills also feature automatic tool changers (ATC) for increased efficiency.
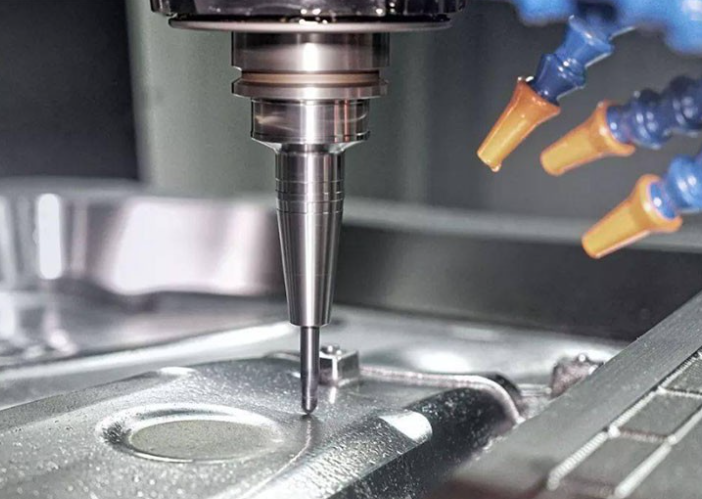

How Desktop CNC Milling Machine Work
The process of using a desktop CNC mill begins with a design created in CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. This design is then converted into G-code using CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software, which tells the CNC mill how to move and what operations to perform. Once the machine is set up with the appropriate material and tooling, the milling process begins. The software precisely controls the movements of the spindle and cutting tool, allowing for intricate cuts and detailed finishes.
Advantages of Desktop CNC Mills
- Cost Efficiency: Desktop CNC mills are significantly cheaper than industrial models, making them an attractive option for hobbyists and small businesses.
- Space-Saving: These machines are designed to fit in small workshops or even home garages, without sacrificing functionality.
- Accessibility: With user-friendly software and abundant online resources, desktop CNC mills are accessible to beginners and professionals alike.
- Versatility: Capable of working with a variety of materials, desktop CNC mills are suitable for a wide range of applications, from metalworking to woodworking.
Comparison of Desktop CNC Mill with Other Machine Tools
To fully appreciate the benefits of desktop CNC mills, it’s helpful to compare them with other types of milling machines:
Desktop CNC Mills vs. Industrial CNC Mills
- Size and Cost: Desktop CNC mills are compact and affordable, while industrial CNC mills are larger and more expensive.
- Material Capability: Industrial models can handle tougher materials and more demanding tasks.
- Automation: Industrial machines often have more automation features, such as automatic tool changers, while desktop CNC mills are more focused on flexibility and ease of use.
CNC Routers vs. Desktop CNC Mills
- Material and Precision: CNC routers are best for softer materials like wood and plastics, with less precision. Desktop CNC mills offer higher precision and can handle a variety of materials, including metals.
- Applications: CNC routers are ideal for large, flat workpieces, while desktop CNC mills excel at detailed, small-scale projects.
CNC Lathes vs. Desktop CNC Mills
- Function: CNC lathes are designed for turning operations to create round parts, while desktop CNC mills are versatile, handling a range of shapes and features.
- Precision: Both offer high precision, but desktop CNC mills are better suited for creating complex geometries.
Desktop CNC Mills vs. Manual Mills
- Automation and Precision: Desktop CNC mills provide automated control for consistent precision, whereas manual mills rely on the operator’s skill.
- Ease of Use: Desktop CNC mills are easier to use for beginners, thanks to software control, while manual mills require more hands-on experience.
Desktop CNC Mills vs. Tabletop Milling Machines
- Automation and Control: Desktop CNC mills use computer software for automation and complex designs, whereas tabletop milling machines are often manually operated or have limited CNC capabilities.
- Precision and Versatility: Desktop CNC mills offer higher precision and can handle a wider range of materials and shapes compared to tabletop milling machines, which are generally used for simpler tasks.
Getting Started with a Desktop CNC Mill
If you’re new to CNC milling, getting started with a desktop CNC mill is relatively straightforward. Here are some basic steps to help you begin:
- Choose the Right Machine: Select a desktop CNC mill that fits your needs, considering factors like material compatibility, precision, and budget.
- Set Up Your Workspace: Ensure your workspace is safe and well-organized, with enough room for the machine and materials.
- Learn the Software: Familiarize yourself with the CAD/CAM software used to design and program the CNC mill.
- Start with Simple Projects: Begin with basic projects to learn the basics of CNC milling and build your skills gradually.
- Safety First: Always follow safety guidelines to protect yourself and your machine.
Tips and Tricks for Maximizing the Use of a Desktop CNC Mill
- Optimizing Milling Strategies: Use efficient cutting paths and speeds to reduce wear on tools and improve finish quality.
- Tool Maintenance: Regularly clean and inspect your tools to extend their lifespan and maintain precision.
- Troubleshooting: Common issues like tool breakage or misalignment can often be resolved by checking tool settings, material alignment, and software configurations.
- Upgrading Your Machine: Consider upgrading components like the spindle or adding a fourth axis to expand the capabilities of your CNC mill.
Future Trends and Developments
The future of desktop CNC milling is exciting, with advancements in technology continuing to enhance their capabilities. Here are a few trends to watch:
- AI and Machine Learning: AI can optimize machining processes, improving efficiency and reducing errors.
- IoT Integration: Internet of Things (IoT) technology allows CNC mills to communicate with other machines and systems, streamlining production workflows.
- New Materials and Tools: Advances in materials science and tooling technology will expand the range of materials that desktop CNC mills can handle, opening up new possibilities for users.
Conclusion
Desktop CNC mills are powerful tools that offer a range of benefits for hobbyists, small businesses, and educators. With their precision, versatility, and affordability, they are an excellent choice for anyone looking to explore CNC technology or expand their manufacturing capabilities. As technology continues to advance, desktop CNC mills will only become more capable, making them a worthwhile investment for the future.
FAQs
What materials can a desktop CNC mill work with?
Desktop CNC mills can handle a variety of materials, including metals (like aluminum and brass), plastics, and wood. The specific materials depend on the capabilities of the machine and the tools used.
Is a desktop CNC mill suitable for beginners?
Yes, desktop CNC mills are suitable for beginners, especially models that come with user-friendly software and comprehensive instructions. Starting with simple projects can help you learn the basics before moving on to more complex tasks.
What safety precautions should I take when using a desktop CNC mill?
Always wear appropriate safety gear, such as safety glasses and ear protection. Keep your workspace clean and free of obstructions, and ensure you understand how to operate the machine and software before starting a project.











