Laser cutting wood makes creativity and processing simpler, more efficient, and gives designers and artisans greater freedom in their designs. However, not all types of wood perform well in laser cutting. Different woods show unique detail effects after cutting; some have smooth, clean edges, while others may scorch or burn easily. To achieve the best results in your cutting projects, selecting the right wood is crucial.
Choosing the wood type affects not only the precision and edge quality of the cuts but also the ease and efficiency of operation. For example, for detailed engraving, furniture decoration, or model making, selecting the right wood enhances the look and feel of the final product. For beginners or those focused on mass production, choosing the wrong wood can lead to unnecessary challenges. Each type of wood behaves differently with laser cutting, and understanding these characteristics helps make the most of laser cutting’s advantages.
Next, we’ll introduce four types of wood that are best suited for laser cutting. Each wood type brings unique highlights to different projects. We’ll also share some practical cutting tips and key points to consider to help you achieve the best cutting results in your work.

Four Types of Wood Suitable for Laser Cutting
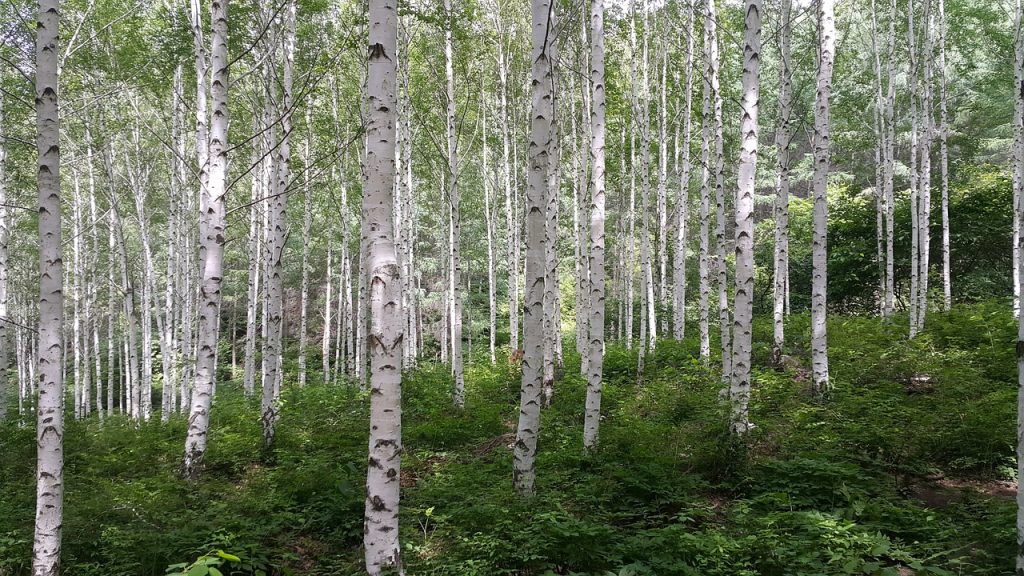
Birch
Birch stands out with its stable properties and fine grain, making it a popular choice for laser cutting. With moderate strength, birch cuts smoothly and leaves clean edges with minimal scorching, ideal for delicate engravings, model making, and small furniture. Its light color preserves natural, sharp edges after cutting and rarely shows burn marks, capturing design details well. Plus, birch is affordable, making it suitable for large-scale projects.
- Application: Great for decorative engraving, custom wood items, and model making.
- Recommended cutting thickness: 3-6 mm.
- Tip: Adjust laser power to avoid excessive scorching, and use air assist to reduce smoke for clean cuts.
Walnut
Walnut’s hard texture and unique dark grain suit high-end products and art pieces. Laser-cut walnut reveals clear patterns and layered contrast, perfect for products needing intricate textures. Since walnut is dense, cutting takes more power and is slower, but the finished result is durable and beautiful.
- Application: Ideal for high-end furniture, artwork, decorative items, and gift packaging.
- Recommended cutting thickness: 3-6 mm; handle thicker materials carefully.
- Tip: Use a high-power laser and slow down the speed to achieve crisp edges.
Cherry
Cherry wood, with its elegant reddish-brown tone and naturally fine grain, is a favorite for projects requiring high visual appeal. Laser cutting beautifully enhances cherry’s color and wood grain, making it perfect for high-aesthetic projects. Cherry’s smooth texture results in clean edges, ideal for small furniture, home décor, and gift packaging.
- Application: Small home items, gift boxes, artistic décor, office supplies.
- Recommended cutting thickness: 3-5 mm.
- Tip: Control laser speed and power to prevent overheating and preserve cherry’s natural color.
Plywood
Plywood offers an affordable option for laser cutting, with high strength and low cost, making it popular for model making, structural parts, and decorative pieces. When choosing plywood, use non-toxic, glue-free materials to avoid harmful gases. Though dense, plywood cuts easily, which makes it a great choice for beginners.
- Application: Models, building parts, functional pieces, small household items.
- Recommended cutting thickness: 4-8 mm.
- Tip: Adjust power and speed properly, and use air assist to reduce burning for smooth edges.
Practical Tips: How to Achieve the Best Laser Cutting Results
To get the best results in laser cutting, understanding and optimizing each operation detail is essential. Here are some practical tips for laser cutting wood:
Adjust Laser Power and Speed
For thinner wood, using lower laser power and higher cutting speed reduces scorching. For thicker wood, increasing power and slowing down the speed ensures complete cuts but requires careful heat control to avoid over-burning the edges.
Use Assistive Gas
Using air assist (with a blower or compressed air) during cutting helps minimize smoke residue on edges and produces smoother cuts, especially effective for plywood and hardwood.
Apply Non-PVC Tape
Applying a layer of non-PVC tape on the cutting surface prevents scorch marks on the wood, protecting it and making cleanup easier. This works particularly well for detailed cuts or engraving projects, keeping the wood surface smooth and undamaged.
Choose the Right Laser
CO₂ lasers work best for wood cutting, especially for medium-thickness materials, creating smooth edges. For thinner wood or projects with limited budgets, low-power diode lasers can also deliver satisfactory results.

You Might Also Want to Know About These Questions
Which Types of Wood Are Not Suitable for Laser Cutting?
Laser cutting doesn’t suit all types of wood, especially those with high oil or resin content, like teak, which can leave visible scorch marks and even produce unpleasant odors when cut. Additionally, certain plywood types contain adhesives with formaldehyde or other harmful chemicals that release irritating gases during cutting. It’s best to choose eco-friendly, non-toxic materials or conduct a small test to confirm suitability.
What Is the Ideal Thickness for Laser Cutting Wood?
Ideally, the best thickness for laser-cutting wood is around 3-6 mm, which ensures good cut quality without easily scorching the edges. For thicker wood (over 10 mm), higher-powered lasers and adjusted feed speeds are necessary to achieve clean cuts. Otherwise, thicker materials can yellow at the edges, which affects appearance.
How Can Scorching on Cut Edges Be Avoided?
Scorched edges are a common issue in laser cutting but can be minimized by lowering the laser power or increasing the cutting speed to reduce heat buildup. Applying non-PVC tape on the wood surface before cutting also helps; simply peel it off afterward. Additionally, using air assist to blow away smoke and dust during cutting promotes a cleaner edge.
How to Choose the Right Laser Cutter?
Select a laser cutter based on the thickness and precision requirements of your material. CO₂ lasers are ideal for wood, with 40W or higher power handling most wood-cutting projects effectively. For thicker or harder woods, an 80W or higher laser cutter is recommended for smoother edges and better results. For smaller projects with lower precision needs, lower-power lasers are also a good option.

What Safety Precautions Should Be Taken When Laser Cutting Wood?
Ensure proper ventilation when laser cutting wood to prevent smoke and fumes from building up. Wood is flammable, so monitor the cutting speed to avoid excessive heat buildup and minimize fire risks. Safety goggles and protective shields are essential to protect operators from laser exposure. Finally, regularly clean the machine’s optical components and maintain a tidy workspace to extend the machine’s lifespan and ensure consistent cutting quality.
When laser cutting wood, each type behaves differently. This article has not only introduced four types of wood most suitable for laser cutting but has also provided tips and precautions to consider during the process. We hope this information helps you make the best choices in your projects and achieve ideal cutting results. If you have further questions about equipment selection or parameter settings, feel free to contact us — we’re here to offer detailed advice and support.