In the rapidly evolving world of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining, software is a pivotal component that enhances productivity and precision. For CNC technicians and scholars, having access to high-quality, free CNC software can be immensely beneficial.
So let’s start with a brief overview of what free CNC software is available:
- GRBL
- Fusion 360 for Personal Use
- LinuxCNC
- FreeCAD
- Candle
This article explores the advantages of free CNC software, highlights some popular options in detail, and examines their practical applications.
Main types of CNC Software
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) software is essential in the world of machining, offering various functionalities that streamline the design and manufacturing process. Understanding the different types of CNC software can help users choose the right tools for their needs. Broadly, CNC software can be categorized into the following types:
CAD Software (Computer-Aided Design)
Used for designing and modeling parts and assemblies. CAD software helps users create detailed 2D and 3D models that can be converted into instructions for CNC machines. Examples include AutoCAD and SolidWorks.
CAM Software (Computer-Aided Manufacturing)
Converts CAD designs into machine-readable code (G-code) that controls CNC machines. CAM software is crucial for generating toolpaths and optimizing the machining process. Popular CAM software includes Mastercam and Fusion 360.
Control Software
Directly interfaces with CNC machines to execute G-code and manage machine operations. This software is responsible for controlling the motion of the CNC machine and ensuring precision. Examples are LinuxCNC and GRBL.
Simulation Software
Allows users to test and simulate CNC operations in a virtual environment before actual machining. This helps in verifying designs and detecting potential issues. Software like Vericut is used for simulation purposes.
G-code Senders
Specialized software for sending G-code commands to CNC machines. These programs facilitate the communication between the computer and the CNC machine, enabling the execution of machining tasks. Candle is an example of a G-code sender.
By understanding these categories, CNC technicians and scholars can better navigate the diverse landscape of CNC software and select tools that best meet their requirements.
Benefits of Free CNC Software
Free CNC software offers several significant benefits:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduces financial burdens for small businesses and educational institutions.
- Accessibility: Enables more users to experiment and learn without high software costs.
- Community Support: Often comes with a robust online community for troubleshooting and advice.
- Regular Updates: Many free programs are updated frequently, incorporating the latest advancements.
Popular Free CNC Software Options
GRBL
GRBL is an open-source firmware designed to run on Arduino boards, enabling them to control CNC machines. It’s widely used in small-scale and hobbyist CNC applications due to its simplicity and reliability.
Applications:
- Desktop CNC Mills: Ideal for small desktop milling machines.
- Laser Cutters: Commonly used in hobbyist laser cutting setups.
- 3D Printers: Sometimes adapted for 3D printing applications.
Advantages:
- Simplicity: Easy to set up and configure, making it accessible for beginners.
- Low Cost: Utilizes inexpensive Arduino hardware.
- Flexibility: Supports a range of machine types and configurations.
- Community Support: Extensive documentation and an active user community for troubleshooting.
Fusion 360 for Personal Use
Fusion 360, offered by Autodesk, is a powerful CAD/CAM software that integrates design, engineering, and manufacturing capabilities. The personal use version is free for hobbyists and small businesses.
Applications:
- Prototyping: Excellent for designing and testing prototypes with advanced simulation tools.
- 3D Modeling: Provides sophisticated tools for creating complex 3D models and assemblies.
- CAM Operations: Generates toolpaths for CNC machining, including milling and turning.
Advantages:
- All-in-One Solution: Combines CAD, CAM, and CAE in a single platform.
- Advanced Features: Offers advanced modeling tools, simulation, and cloud collaboration.
- Regular Updates: Frequently updated with new features and improvements.
- Integration: Works seamlessly with various CNC machines and controllers.
LinuxCNC
LinuxCNC is an open-source software used to control CNC machines on Linux-based systems. Known for its high flexibility and robustness, it is suitable for complex machining tasks.
Applications:
- Mills, Lathes, and Routers: Ideal for a wide range of CNC machinery.
- Custom Machines: Adaptable for specialized and custom CNC setups.
- Industrial Applications: Used in both hobbyist and professional environments.
Advantages:
- Flexibility: Supports numerous machine types and configurations.
- Customization: Highly configurable to suit specific needs and hardware setups.
- Community and Documentation: Comprehensive support from a dedicated community and extensive documentation.
- Real-Time Performance: Offers real-time control and high precision.
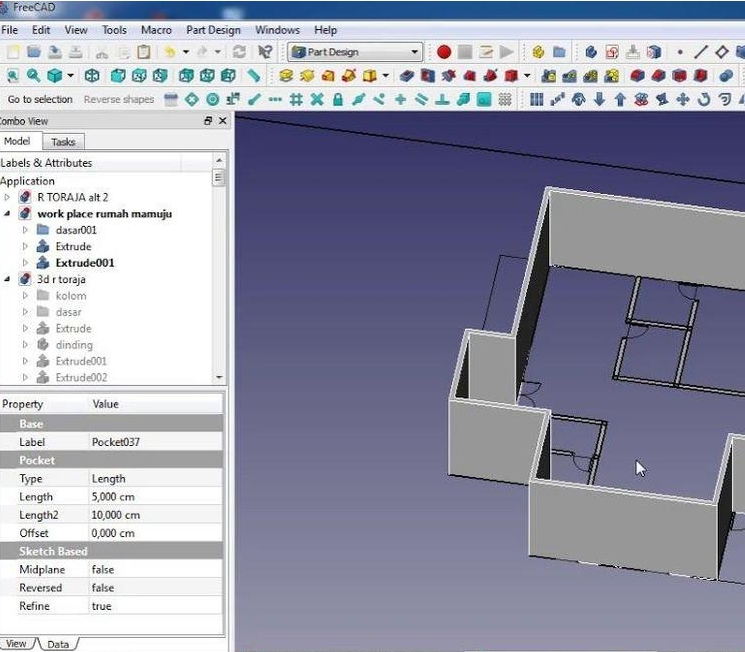
FreeCAD
FreeCAD is an open-source parametric 3D CAD modeler that supports various plugins and workbenches for CNC applications. Although it is not exclusively a CNC software, it provides significant functionality for design and machining.
Applications:
- Design and Prototyping: Useful for creating detailed 3D models and designs.
- CNC Machining: Supports G-code generation and integration with CNC tools via plugins.
- Educational Use: Ideal for teaching CAD principles and CNC operations.
Advantages:
- Parametric Design: Allows for easy modifications and iterations of designs.
- Extensibility: Enhanced with numerous plugins for specific CNC functions.
- User-Friendly Interface: Accessible for both beginners and advanced users.
- Community Development: Constant updates and improvements from the open-source community.
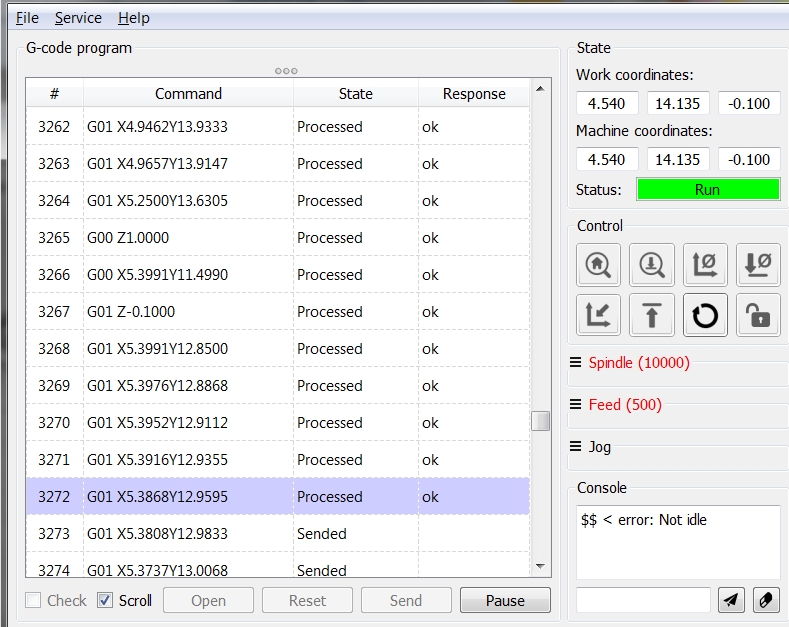
Candle
Candle is a simple G-code sender designed for controlling CNC machines. It is especially user-friendly and targeted towards hobbyists.
Applications:
- Basic CNC Operations: Suitable for managing simple CNC tasks and operations.
- Hobbyist Machines: Commonly used with hobbyist and small CNC setups.
- G-Code Sending: Efficiently sends G-code to CNC machines for execution.
Advantages:
- Ease of Use: Intuitive interface, making it accessible for newcomers to CNC.
- Lightweight: Minimal system requirements and straightforward installation.
- Focused Functionality: Specializes in G-code sending with essential features for operation.
Applications of Free CNC Software
Free CNC software finds applications in various contexts:
- Educational Settings: Enables students and educators to gain hands-on experience without high software costs.
- Prototyping: Helps small businesses and individuals create prototypes and test designs without a significant investment.
- Hobby Projects: Ideal for DIY enthusiasts working on personal projects or small-scale productions.
Choosing the Right Software
When selecting free CNC software, consider these factors:
- Compatibility: Ensure the software is compatible with your CNC hardware and operating system.
- Features: Evaluate if the software provides the necessary features for your specific needs, such as design tools, simulation, and G-code generation.
- Community and Support: Look for software with an active user community and available support resources.
Conclusion
Free CNC software can be a game-changer for technicians and scholars, offering powerful tools and opportunities for learning and innovation. By understanding the available options and their applications, users can make informed decisions and harness the full potential of CNC technology without breaking the bank.
References
- GRBL Official Website
- Fusion 360 for Personal Use
- LinuxCNC Official Website
- FreeCAD Official Website
- Candle Official Website










