CNC machines are everywhere in modern manufacturing, from aerospace to electronics. They’ve changed the way we design, prototype, and manufacture products by giving us unparalleled precision, efficiency, and flexibility.
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machine is a sophisticated manufacturing tool that utilizes computer programming to control machine tools. This technology allows for precision and automation in various manufacturing processes, making it essential in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics. CNC machines can perform a wide range of tasks including cutting, drilling, and milling, all with high accuracy and repeatability. Understanding CNC machines is crucial for those involved in modern manufacturing, as they play a pivotal role in improving production efficiency and product quality.
Want to know more about what is a CNC machine? Let’s unravel the mystery behind this cutting-edge technology!
A Brief History of CNC Machine Tools
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machine tools have been around since the mid-20th century, when they revolutionized manufacturing by replacing manual control with automated control. Before CNC, skilled operators controlled machine tools using handwheels and levers. It was time-consuming, and it was prone to human error and inconsistencies.
The idea of automated control started to take shape during World War II, when precision and efficiency in manufacturing became critical. John T. Parsons is often credited with developing the first numerical control (NC) machine in the late 1940s. He used punched cards to control machine movements, which laid the foundation for modern CNC technology.
By the 1950s, MIT (the Massachusetts Institute of Technology) partnered with the U.S. Air Force to create the first true CNC machine. This machine used a computer to control the tool paths, which made it possible to do more complex and precise machining. CNC technology transformed manufacturing by giving us unprecedented levels of accuracy, repeatability, and automation.
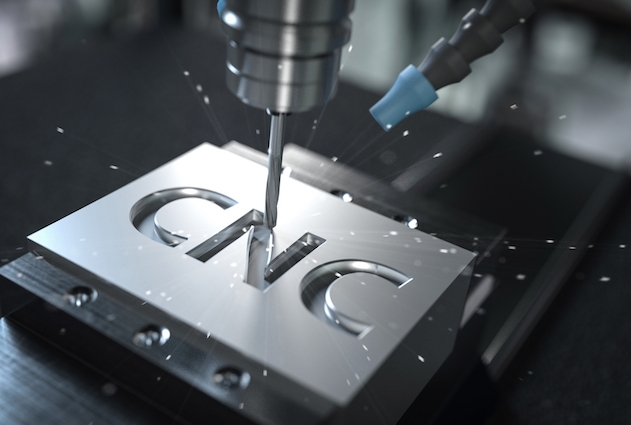

What is CNC?
CNC stands for Computer Numerical Control. It’s the automated control of machining tools and 3D printers by a computer. A CNC machine reads a digital file that contains instructions for moving the machine’s components. These instructions, called G-code, tell the tool how fast to move, where to go, and how fast to feed into the workpiece.
The main components of a CNC system are:
– Computer: The brain of the CNC system. It runs special software that interprets the digital instructions.
– Controller: The interface between the computer and the machine. It translates the digital instructions into signals that control the machine’s motors and drives.
– Drive Motors: These motors move the machine’s components along the X, Y, and Z axes and rotate the spindle.
– Machine Tool: The part of the CNC machine that does the actual machining. It cuts, drills, mills, and so on.
CNC technology gives us high precision and repeatability, which is why it’s so important in modern manufacturing.
What is a CNC Machine?
A CNC machine is a highly automated tool controlled by a computer running a CNC program. These machines can do lots of different things, like cutting, drilling, milling, turning, and more. There are different types of CNC machines, each designed for specific tasks and materials.
Here’s how a CNC machine works:
Design the Part: Use CAD software to create a digital model of the part.
Generate the CNC Program: Use CAM software to turn the CAD model into a CNC program. This program tells the machine where to move and what machining operations to do.
Load the Program: Transfer the CNC program to the machine’s controller.
Set Up the Machine: Put in the right tools, secure the workpiece, and configure the machine settings.
Run the Program: The controller tells the machine tool to follow the paths in the program and remove material to make the part.
The main functions of a CNC machine are:
– Cutting: Removing material from a workpiece to make a shape.
– Drilling: Making holes in a workpiece with precise diameters and depths.
– Milling: Removing material from a workpiece with rotary cutters to make complex shapes and features.
– Turning: Rotating a workpiece on its axis while a cutting tool removes material to make cylindrical parts.
CNC machines can work with many different materials, like metals, plastics, composites, wood, and more. They’re used in lots of industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, medical, and consumer goods.
The Importance of CNC Machining
CNC machining is critical in modern manufacturing because it offers so many advantages. It gives us high precision, consistency, and efficiency when making complex parts. CNC machines can run 24/7, which makes us more productive and reduces lead times. They also reduce human error, so we get high-quality parts with fewer defects.
6 Common Types of CNC Machines
1. CNC Milling Machines: Used for cutting and drilling.
2. CNC Lathes: Used for turning operations.
3. CNC Routers: Used for cutting various materials like wood and plastics.
4. CNC Plasma Cutters: Used for cutting metal with a plasma torch.
5. CNC Electric Discharge Machines (EDM): Used for shaping hard metals and creating complex cavities.
6. CNC Laser Cutters: Used for precise cutting using a focused laser beam.
How Does a CNC Machine Tool Work?
CNC machine tools work by following a set of programmed instructions to perform specific machining operations. The process involves several key steps:
-
- Design Creation: The process begins by creating a detailed design of the part using CAD software. This digital model includes all the dimensions, shapes, and features of the part.
-
- CNC Program Generation: The CAD model is then converted into a CNC program using CAM software. This program contains detailed instructions for the machine, such as tool paths, cutting speeds, and feed rates.
-
- Program Loading: The CNC program is transferred to the machine’s controller, which interprets the instructions and directs the machine tool accordingly.
-
- Machine Setup: The machine is prepared for operation by installing the necessary tools, securing the workpiece, and configuring the machine settings. This may involve adjusting the position of the worktable, setting the tool offsets, and calibrating the machine.
-
- Program Execution: The controller directs the machine tool to follow the specified paths and perform the machining operations. The tool moves along multiple axes, removing material to create the desired shape.
-
- Monitoring and Adjustments: Throughout the machining process, feedback systems monitor the machine’s movements and make real-time adjustments to ensure accuracy. This may involve compensating for tool wear, thermal expansion, and other factors that can affect precision.
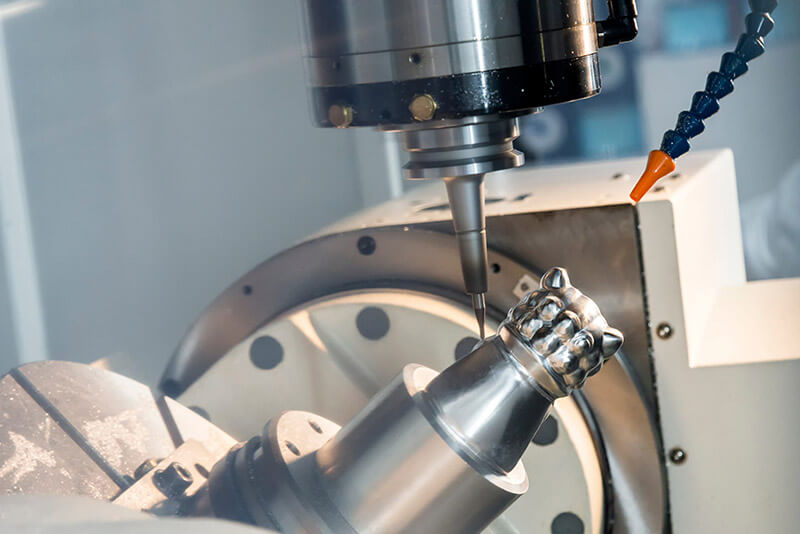

How Does CNC Milling Work?
CNC milling is a process where a cutting tool is rotated while the workpiece is moved in multiple axes to shape the part as specified in the CNC program. Milling can be done on a variety of materials including metals, plastics, and composites, allowing for the creation of intricate designs and complex geometries.
How Does CNC Turning Work?
CNC turning is a process where the workpiece is rotated while a stationary cutting tool removes material. This process is primarily used to create cylindrical parts such as shafts and rods. The CNC program controls the speed and movement of the workpiece and tool to achieve the desired shape and dimensions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of CNC Machining
Advantages:
– High precision and accuracy
– Consistent quality
– Increased production speed
– Reduced human error
– Ability to create complex parts
Disadvantages:
– High initial cost
– Requires skilled operators and programmers
– Maintenance can be expensive
– Limited by the capabilities of the machine and tools
What Are the Most Common Cutting Tools for CNC Machining?
Common cutting tools used in CNC machining include:
– End mills
– Drills
– Turning tools
– Taps
– Reamers
– Boring bars
These tools are made from materials such as high-speed steel (HSS), carbide, and ceramics to withstand the demands of cutting various materials.
What Materials Can Be CNC Machined?
CNC machines can handle a wide range of materials, including:
– Metals (aluminum, steel, titanium, etc.)
– Plastics (acrylic, nylon, polycarbonate, etc.)
– Composites (carbon fiber, fiberglass, etc.)
– Wood
– Foam
CNC Machining Parts with Geometric Complexity: What are the Design Limitations?
Designing parts with CNC machining in mind requires an understanding of certain limitations. Deep cavities, sharp internal corners, and complex undercuts can be problematic. You also need to consider the size of the part and the accessibility of the tool. Using fillets instead of sharp corners and minimizing deep cuts can help you design parts that can be manufactured.

What Are the Trends in the CNC Machining Industry?
The CNC machining industry is constantly evolving. Technological advancements and changing market demands are driving this evolution. Some of the key trends shaping the industry include:
-
- Increased Automation: CNC machining is becoming more automated. This includes the use of robotics and automated systems. Automation improves efficiency, reduces labor costs, and increases precision.
-
- Integration of IoT: The Internet of Things (IoT) is being integrated into CNC machines. This allows for real-time monitoring, data collection, and optimization. IoT-enabled machines can predict maintenance needs and improve overall productivity.
-
- Improved Software Capabilities: Advancements in CAD/CAM software are making it easier to design and program complex parts. Improved simulation and verification tools help ensure accuracy and reduce errors.
-
- Additive Manufacturing: The combination of CNC machining and additive manufacturing (3D printing) is gaining popularity. This hybrid approach allows for greater design flexibility and the production of complex geometries.
-
- Sustainability: There is an increasing emphasis on sustainable machining practices. This includes the use of recyclable materials, energy-efficient machines, and waste reduction strategies.
-
- Customization and Small Batch Production: CNC machining is being used more frequently for customized and small batch production. The flexibility and precision of CNC machines make them ideal for producing unique and one-off products.
As these trends continue to develop, the CNC machining industry will become more efficient, versatile, and better equipped to meet the demands of modern manufacturing.
CNC machining remains a key part of modern manufacturing, offering unrivaled precision and efficiency in producing a wide range of products. As technology advances, the capabilities and applications of CNC machines will continue to grow, driving innovation across a range of industries.
FAQs
To select the best CNC machine type, consider the material, complexity of the task, and production volume. Different CNC machines are better suited for different applications. For example, milling machines are great for making intricate parts, while lathes are ideal for making symmetrical objects. Consider the material you’ll be working with, how precise you need to be, and how many parts you need to make. Talk to experts and read machine specs to help you make an informed decision.
Yes, a 3D printer is a type of CNC machine because it uses computer numerical control to add material layer by layer to create an object. 3D printers and CNC machines both use computer-aided design (CAD) files to produce objects. However, the main difference is in how they work: 3D printers are additive, building objects layer by layer, while traditional CNC machines are subtractive, removing material to achieve the desired shape. Understanding this difference helps you choose the right tool for your manufacturing needs.
CNC machines are not inherently hard to operate, but they do require proper training and practice. Modern CNC machines come with advanced software that makes programming them easier. With the right training, operators can quickly learn how to run these machines effectively. The key is to understand the basics of CNC programming, machine setup, and safety procedures. Practice and staying up to date with technology also make operating them easier.
CNC machining is not completely automated; it requires human supervision for programming, setup, and maintenance. CNC machines automate many parts of the manufacturing process, such as cutting, drilling, and finishing. However, humans are needed to program the machine, set it up, and do routine maintenance. Humans also play a critical role in quality control, making sure the finished parts meet the required specifications. This combination of automation and human expertise ensures CNC machining performs at its best and produces high-quality parts.











