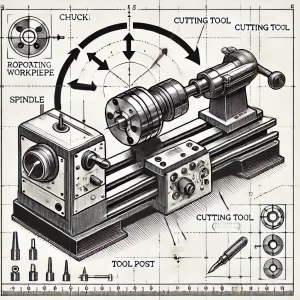
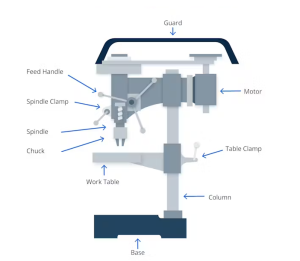
Metalworking is more than just a craft; it’s the backbone of modern industry. From the smallest components in your smartphone to the towering structures of skyscrapers, metalworking is at the heart of manufacturing. For anyone looking to dive into this fascinating world, understanding the techniques, tools, and trends is essential.
Metalworking involves shaping, cutting, and joining metals to create components, tools, and structures. It encompasses a range of techniques including forging, welding, and CNC machining, making it a versatile skill set in industries from automotive to aerospace.
In this guide, we will explore everything you need to know about metalworking, providing you with a strong foundation whether you’re a beginner or looking to enhance your skills as a seasoned engineer.
What is Metalworking?
Metalworking is the process of creating usable items and structures from metal, involving various techniques like forming, cutting, joining, and finishing. It’s an ancient craft that has evolved over thousands of years, playing a crucial role in human development from the Bronze Age to the Industrial Revolution, and now into the age of digital manufacturing.
Brief History of Metalworking
The history of metalworking is as rich as the metals themselves. Over 7,000 years ago, early humans began hammering copper into shapes for tools and ornaments. The Bronze Age, starting around 3300 BCE, saw the advent of stronger tools and weapons made by alloying copper with tin. Fast forward to the Iron Age, around 1200 BCE, when the ability to smelt iron ore changed the face of agriculture and warfare. The Middle Ages and Renaissance periods introduced more sophisticated techniques and machinery, paving the way for the Industrial Revolution’s steam-powered factories. Today, metalworking is a highly specialized field involving advanced technologies like CNC machining, 3D printing, and robotics.
Metalworking Techniques
Forming Techniques
Forming is a metalworking process that reshapes metal without adding or removing material. The most common forming techniques include:
- Forging: A process where metal is heated and hammered into shape. It’s widely used for parts that need high strength, such as automotive components and tools. According to the Forging Industry Association, 90% of all metal components in cars are forged.
- Rolling: Involves passing metal between rollers to reduce thickness. Hot rolling is used for large pieces like beams, while cold rolling creates thinner sheets for applications like car bodies.
- Extrusion: Metal is forced through a die to create long objects with a fixed cross-section, like pipes and rods. Aluminum is a popular choice for extrusion due to its malleability and strength-to-weight ratio.
- Bending: Techniques like air bending and bottoming are used to shape metal sheets into desired angles. CNC press brakes are commonly used for precision bending in industries ranging from aerospace to consumer electronics.
Cutting Techniques
Cutting processes remove material from a workpiece to create the desired shape and size. Key cutting techniques include:
- Turning: Performed on a lathe, turning involves rotating the workpiece while a cutting tool removes material. It’s essential for creating cylindrical parts like shafts and pulleys.
- Milling: This process uses rotary cutters to remove material, allowing for more complex shapes and profiles. CNC milling machines can achieve precision tolerances, making them indispensable in high-tech manufacturing sectors.
- Drilling: Used to create round holes in a workpiece, drilling is a straightforward yet crucial operation in metalworking. With the right drill bit and feed rate, even hardened steel can be drilled accurately.
- Sawing: Bandsaws and circular saws are common tools for cutting metal to size. They are efficient and capable of cutting a wide range of materials from aluminum to stainless steel.
Joining Techniques
Joining is the process of assembling metal components into a single piece. It includes:
- Welding: The most widely used method, welding involves melting the edges of metal pieces to fuse them together. Techniques like MIG (Metal Inert Gas) and TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding are popular for their strength and versatility.
- Soldering and Brazing: These methods use a filler metal to bond components without melting the base materials. They are ideal for delicate electronics and plumbing.
- Riveting: A non-thermal process where metal fasteners called rivets are used to join pieces. Riveting is often used in aircraft construction due to its reliability and strength.
Finishing Techniques
Finishing enhances the appearance and functionality of metal products:
- Grinding: This process uses abrasives to remove surface imperfections, ensuring a smooth finish.
- Polishing: Polishing brings out a shiny surface, often used for aesthetic purposes or to reduce friction.
- Coating: Coatings protect metal from corrosion and wear. Common coatings include galvanizing for steel and anodizing for aluminum.
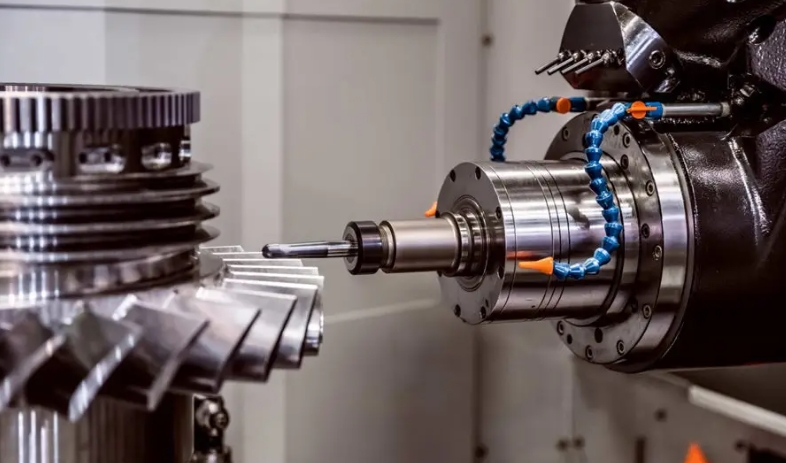
Essential Tools and Equipment for Metalworking
Machine Tools
Machine tools are essential for any metalworking operation. Lathes, milling machines, and drill presses form the core of most workshops. According to a 2023 survey by the American Machinist, CNC machines are becoming increasingly prevalent, with 75% of shops planning to invest in new CNC technology within the next five years. These machines allow for precision, repeatability, and the ability to produce complex parts that are impossible to make manually.
Hand Tools
Hand tools are equally important, especially for finishing and fine-tuning workpieces. A well-equipped toolbox might include hammers, files, chisels, and wrenches. Proper use and maintenance of these tools can significantly impact the quality of work and longevity of the tools themselves.
Cutting Tools
Cutting tools made from high-speed steel, carbide, or ceramics are critical for efficient material removal. The choice of cutting tool depends on the material being machined and the desired finish. Innovations in tool coatings, such as titanium nitride (TiN) and diamond-like carbon (DLC), have improved tool life and cutting performance.
Safety Equipment
Safety should never be an afterthought. Personal protective equipment (PPE) like gloves, goggles, and helmets is vital to protect against the risks of metalworking. According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), proper PPE can reduce workplace injuries by up to 50%.
Modern Metalworking Technologies
CNC Machining
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining has revolutionized the metalworking industry. Now, CNC machines automate the control of tools with precise coding, allowing for the creation of complex parts with minimal human intervention. This not only enhances efficiency but also ensures consistent quality. In fact, CNC machining accounts for nearly 20% of the global machine tool market, reflecting its importance in modern manufacturing.
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, is a rapidly growing area within metalworking. By building parts layer by layer from metal powders, this technology offers unprecedented design freedom and the ability to create complex geometries that are impossible with traditional methods. The global market for metal 3D printing is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 28.8% from 2021 to 2028, demonstrating its rising influence in sectors like aerospace and medical devices.
Automation and Robotics in Metalworking
Automation and robotics are enhancing productivity and safety in metalworking shops worldwide. From robotic welders to automated material handling systems, these technologies reduce labor costs and improve precision. A report by McKinsey & Company suggests that automation could save manufacturers up to 25% in production costs by 2030.
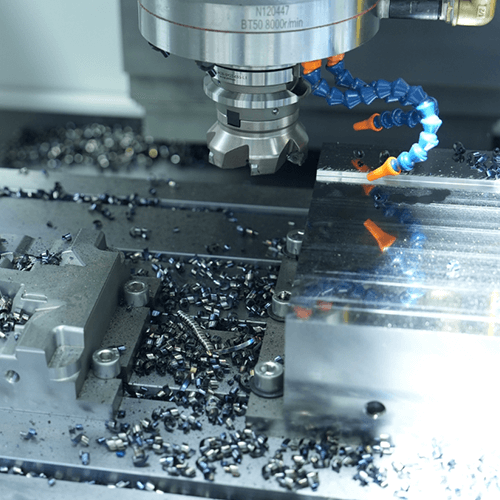
Trends and Innovations in Metalworking
Sustainable Metalworking Practices
Sustainability is becoming a key consideration in metalworking. Techniques like recycling scrap metal, using energy-efficient machines, and adopting cleaner production processes are reducing the environmental impact of metalworking. According to the World Steel Association, the steel industry has reduced energy consumption per ton of steel produced by 60% over the past 50 years, highlighting the industry’s commitment to sustainability.
Advanced Materials
The development of advanced materials such as composites and superalloys is pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in metalworking. These materials offer superior strength, corrosion resistance, and heat tolerance, making them ideal for high-performance applications in aerospace, automotive, and energy sectors.
Digital Transformation in Metalworking
Digital technologies are transforming metalworking operations, making them smarter and more efficient. The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and big data analytics allows for predictive maintenance, optimized production schedules, and enhanced quality control. According to a survey by PwC, 72% of manufacturing companies are already implementing or planning to implement Industry 4.0 technologies.
How to Level Metalworking in Project Zomboid
Introduction to Metalworking in Project Zomboid
In the survival game “Project Zomboid,” metalworking is a valuable skill that allows players to craft and repair metal items, improving their chances of survival in a post-apocalyptic world. Mastering metalworking in the game involves gathering materials, learning recipes, and efficiently using tools.
Steps to Level Up Metalworking
To level up metalworking in “Project Zomboid,” players should focus on several key activities:
- Gathering Materials: Scavenge scrap metal, pipes, and other resources from buildings and vehicles.
- Crafting Tools: Create basic metalworking tools like hammers and saws, and find propane torches for advanced crafting.
- Reading Skill Books: Increase experience gain by reading metalworking books found in libraries and bookstores.
- Crafting Items: Practice by making metal fences, doors, and containers, which provide good experience.
- Disassembling Objects: Disassemble lockers, car wrecks, and other metal objects for both materials and experience.
- Maximizing Efficiency: Use propane torches wisely and recycle scrap to make the most of limited resources.
Benefits of High-Level Metalworking
Higher levels in metalworking enable players to craft more durable items and structures, enhancing their defenses and survival capabilities.
Tips and Tricks for Efficient Metalworking
Look for metalworking resources in industrial areas and garages, where tools and scrap are plentiful. Avoid wasting materials on low-experience items and focus on crafting and disassembling to maximize gains.
Practical Tips for Aspiring Metalworking Engineers
Starting a Career in Metalworking
A career in metalworking can be highly rewarding. Start by pursuing relevant education, such as a degree in mechanical engineering or a vocational course in welding or machining. Hands-on experience is invaluable, so seek internships or apprenticeships in metalworking shops.
Choosing the Right Metalworking Equipment
When buying equipment, consider the type of work you plan to do. Research different brands, read reviews, and compare features to find the best fit for your needs and budget.
Best Practices for Metalworking
To achieve high-quality results, maintain your tools and machines regularly, follow safety protocols, and keep up with industry trends to stay competitive.
Continuing Education and Professional Development
The metalworking industry is constantly evolving, so continuous learning is key. Attend workshops, take online courses, and network with other professionals to keep your skills sharp and your knowledge up-to-date.
Conclusion
Metalworking is a dynamic and essential field that offers countless opportunities for innovation and growth. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to expand your skills, understanding the fundamentals of metalworking will serve you well in any engineering career. As technology advances, the possibilities in metalworking are virtually limitless. Embrace the challenges and enjoy the journey as you craft the future.
FAQs
What are the basic tools needed for metalworking?
Basic tools for metalworking include a hammer, anvil, forge, tongs, chisels, and files. For more advanced work, machine tools like lathes, milling machines, and welders are essential.
What is the difference between forging and casting?
Forging involves shaping metal using compressive forces, typically at high temperatures, whereas casting involves pouring molten metal into a mold where it solidifies.
What safety precautions should I take when metalworking?
Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, goggles, and hearing protection. Follow proper procedures for handling tools and machinery to avoid accidents.