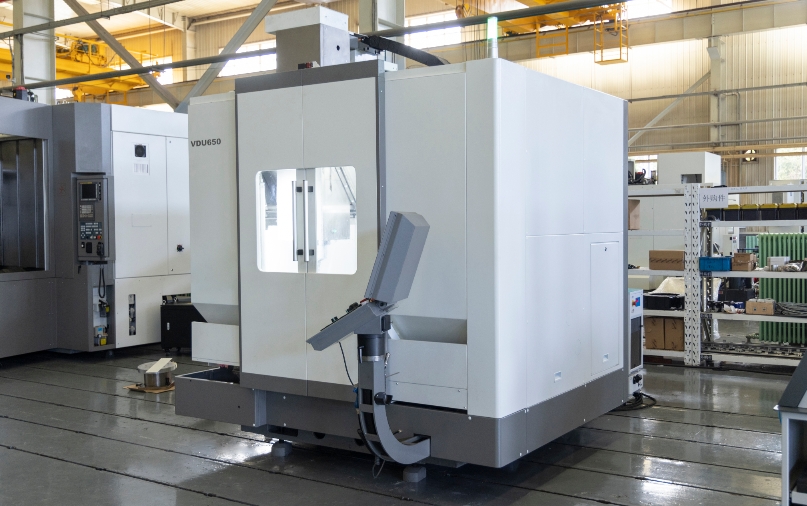
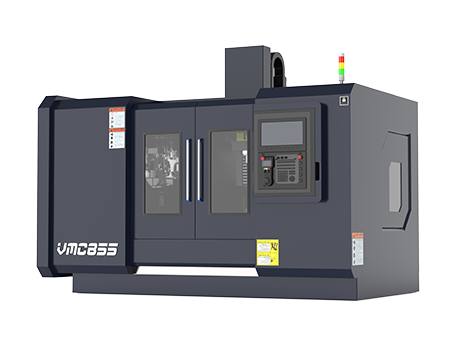
In modern manufacturing, vertical machining centers and horizontal machining centers are two commonly used CNC machines. This article provides a detailed comparison of Vertical Machining Center (VMC) vs Horizontal Machining Center (HMC) and offers some selection guidelines to help you make the right decision based on your machining needs.
What is a Vertical Machining Center?
A Vertical Machining Center (VMC) has its spindle axis set vertically, perpendicular to the worktable. It is mainly used for machining complex parts such as plates, disks, molds, and small-sized housings. A VMC can perform milling, boring, drilling, tapping, and thread cutting operations.
Features
Easy Operation: Vertical machining centers offer simple clamping and easy operation, making program debugging convenient.
Better Visibility: With an open design and minimal obstructions, operators can easily observe the contact between the tool and the workpiece.
Space Efficient: Their compact structure takes up less floor space.
Cost-Effective: Vertical machining centers are typically much cheaper than horizontal machining centers.
Workpiece Types
Vertical machining centers are ideal for machining complex parts such as plates, disks, molds, and small-sized housings.

What is a Horizontal Machining Center?
A Horizontal Machining Center (HMC) has its spindle axis set parallel to the worktable, primarily used for machining box-type parts. After clamping the workpiece once, the machine automatically selects different tools, adjusts spindle speeds, and completes multiple operations on various faces of the workpiece.
Features
Easy Chip Removal: The horizontal layout of the worktable and spindle allows chips to fall away naturally due to gravity.
Suitable for Large Workpieces: The horizontal design isn’t limited by column height or tool change mechanisms, enabling the machining of larger parts.
Workpiece Types
Horizontal machining centers are ideal for machining helical parts, cylindrical cams, box-type components, and complex curved surfaces.
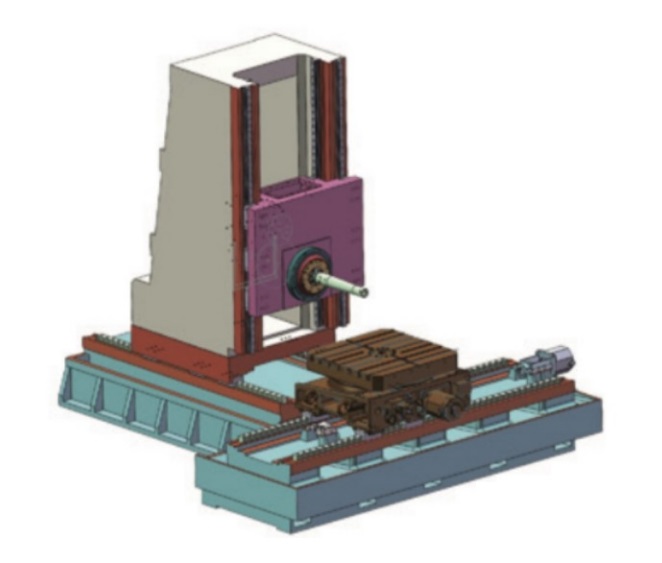
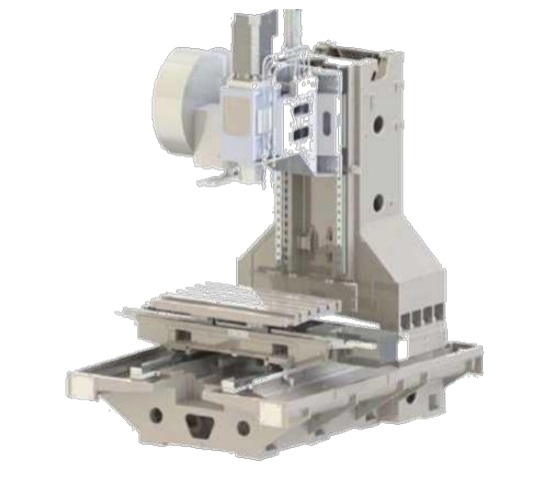
Structural Differences
The earlier points highlight some distinctions between vertical and horizontal machining centers. Let’s delve into their structural differences.
Spindle Structure Differences:
Vertical Machining Centers (VMC): VMCs often feature an A-frame column to achieve the necessary rigidity, making them robust. Some VMCs have a moving column design, where the worktable moves in either the X or Y direction, and the column moves in the other direction, requiring powerful drive motors for the column.
Horizontal Machining Centers (HMC): HMCs always have a moving column. In an HMC, a T-shaped column moves along the X-axis, while an inverted T-shaped column moves along the Z-axis.
Worktable Differences:
VMC Worktable: Typically, VMC worktables have a T-slot cross-slide structure. Two sets of movement mechanisms handle the perpendicular movements of the worktable. The X-axis feed worktable sits atop the Y-axis feed guideway.
HMC Worktable: HMC worktables only move in the X or Y direction and are usually rotary. They can also be equipped with an exchangeable double worktable.
Tool Magazine Types:
VMC: Commonly use hat-type and disc-type tool magazines.
HMC: Usually employ chain-type tool magazines.
Axis Differences:
VMC: Typically have three-axis linkage, which can be expanded to four or five axis.
HMC: Standard configuration includes four-axis three-linkage, expandable to five axis.
How to Choose
If you still can’t fully distinguish between vertical and horizontal machining centers from the information above, let’s clarify by examining some key purchasing factors.
Workpiece Type:
- For small, precise parts, a vertical machining center might be more suitable.
- For large, complex box-type parts, a horizontal machining center is likely the better choice.
Machining Efficiency:
– If you need high machining efficiency and quick processing of numerous parts, the high-speed and automatic tool change capabilities of a vertical machining center may offer advantages.
Space Constraints:
- Vertical machining centers, with their compact design, are more suitable for smaller workshop spaces.
- Horizontal machining centers have a more complex structure and require more floor space.
Budget:
– Horizontal machining centers generally have a higher price. If you have a limited budget, a vertical machining center might be a more cost-effective option.
Minnuo Vertical and Horizontal Machining Centers
Minnuo, as a professional CNC lathe manufacturer and supplier, we produce and manufacture vertical machining centers and horizontal machining centers, both of which can meet the requirements for precision and speed of machined workpieces. We offer the latest Fanuc 0i-MF(5) system for our CNC control systems, ensuring top-notch machine configurations. Simply choose the right machining center based on your needs, and contact us for discounted prices!
Recommended Articles: What are the key programming distinctions between vertical and horizontal machining centers?