In the realm of modern manufacturing, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines have revolutionized the industry by bringing unparalleled precision, efficiency, and versatility. These machines, controlled by computers to execute pre-programmed sequences of machine control commands, have become integral to a wide range of industries.
The five most common types of CNC machines are CNC Milling Machines, CNC Lathes, CNC Plasma Cutters, CNC Laser Cutting Machines, and CNC Drilling Machines. Each of these machines is uniquely designed to perform specific tasks in manufacturing, from creating intricate geometries to high-speed metal cutting, making them indispensable across various industries.
Whether you’re a seasoned professional or someone exploring the potential of CNC technology, understanding the various types of CNC machines is essential. This knowledge not only helps in making informed decisions when purchasing a machine but also ensures that the right equipment is used for specific tasks, optimizing production and enhancing the quality of the final product.
What Are the 5 Common Types of CNC Machines?
The five most common types of CNC machines are CNC Milling Machines, CNC Lathes, CNC Plasma Cutters, CNC Laser Cutting Machines, and CNC Drilling Machines. These machines are distinct in their design, functionality, and the specific tasks they are best suited for. Below, we explore each type in detail, highlighting their key features, applications, and advantages.
CNC Milling Machines: The Backbone of Precision Manufacturing
CNC milling machines are perhaps the most versatile and widely used CNC machines in manufacturing. They operate by rotating cutting tools to systematically remove material from a stationary workpiece. The ability to precisely control the movement of the cutting tools along multiple axes makes CNC milling machines indispensable for producing complex geometries with tight tolerances.
Key Operations:
- Face Milling: In this operation, the cutting tool’s flat face is used to cut flat surfaces or remove excess material from the workpiece, creating a smooth finish.
- Shoulder Milling: Shoulder milling is used to create vertical or angled surfaces on a workpiece. This operation is crucial for producing parts with multiple planes or intricate designs.
- Slot Milling: Slot milling involves cutting a slot or groove into the workpiece. It is commonly used in the production of keyways, slots for electrical components, or decorative elements.
- Tapping and Drilling: CNC milling machines can also perform drilling and tapping operations, which involve creating holes and threads, respectively. These operations are essential in the assembly of mechanical components, where precision is paramount.
Applications:
CNC milling machines are widely used in industries such as aerospace, where components must meet stringent quality standards, and in the automotive industry, where they are used to produce engine parts, transmission components, and more. They are also crucial in the medical device industry, where precision is critical for patient safety and product effectiveness.
Common Materials:
– Metals (e.g., aluminum, steel, titanium)
– Plastics (e.g., acrylic, polycarbonate)
– Composites
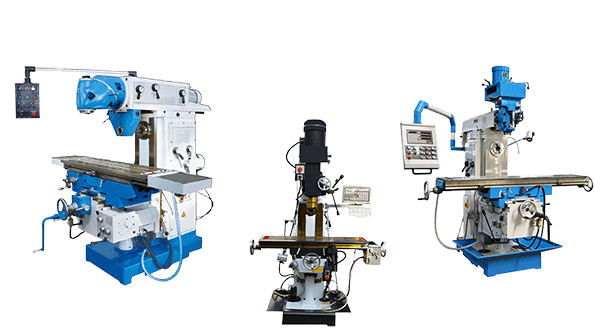
CNC Lathes: Precision in Rotation
CNC lathes are specialized machines designed to produce symmetrical objects through a process known as turning. In a CNC lathe, the workpiece is rotated at high speed while a stationary cutting tool removes material, shaping the workpiece into the desired form. This process is ideal for creating cylindrical parts such as shafts, rods, and bolts.
Key Operations:
- Turning: Turning is the primary operation performed on a CNC lathe, where the cutting tool removes material from the outer diameter of the rotating workpiece. This process is used to create smooth, cylindrical surfaces.
- Threading: Threading involves cutting a helical groove around the circumference of a cylindrical workpiece, creating threads that can be used for screws, bolts, and other fasteners.
- Boring: Boring is used to enlarge an existing hole in the workpiece, ensuring precision and accuracy. This operation is commonly used in the production of engine components, where precise hole diameters are critical.
Applications:
CNC lathes are indispensable in the production of automotive components, such as drive shafts, camshafts, and brake discs. They are also used in the electronics industry to produce connectors and other small, precise components.
Common Materials:
– Metals (e.g., steel, aluminum, brass)
– Plastics (e.g., nylon, PVC)

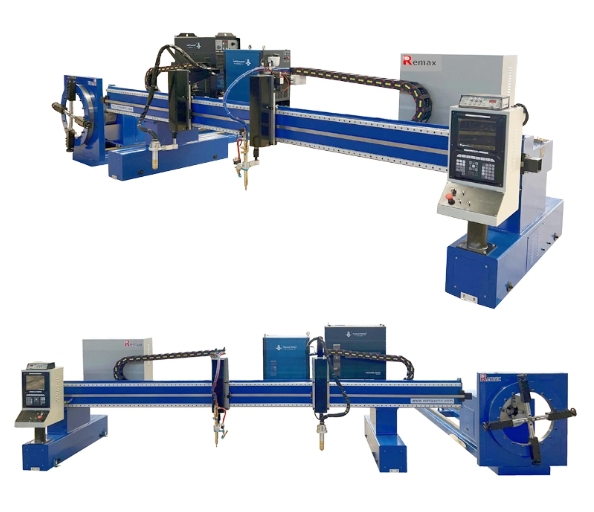
CNC Plasma Cutters: High-Speed Cutting for Metalwork
CNC plasma cutters are known for their ability to cut through metal quickly and precisely using a high-temperature plasma arc. This process is particularly effective for cutting thick metal sheets and is widely used in industries that require fast and accurate metal cutting.
Advantages:
- Speed: Plasma cutting is one of the fastest methods for cutting through metal, making it ideal for high-volume production environments. The ability to quickly produce clean cuts reduces the need for secondary finishing processes, saving time and labor costs.
- Precision: Despite its speed, plasma cutting offers high precision, making it possible to create intricate designs and shapes with minimal material wastage. This precision is especially important in industries like automotive repair, where parts must fit together perfectly.
- Versatility: Plasma cutters can cut through a wide range of conductive metals, including stainless steel, aluminum, and copper, making them versatile tools in metal fabrication.
Applications:
CNC plasma cutters are widely used in the construction industry for cutting structural steel components, in automotive repair shops for cutting body panels and frames, and in metal fabrication shops for creating custom metal parts and products.
Common Materials:
– Stainless steel
– Aluminum
– Copper
– Brass

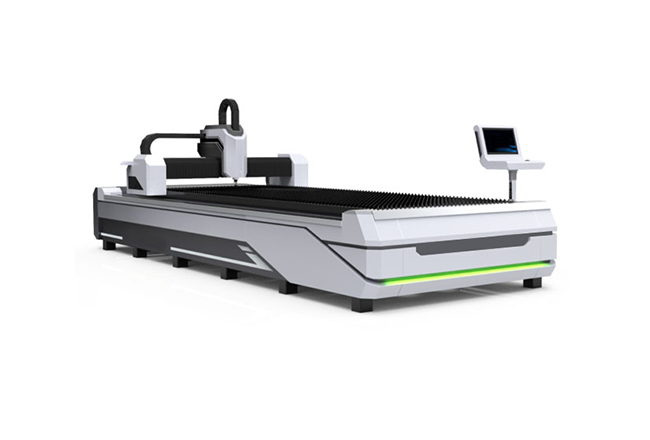
CNC Laser Cutting Machines: Precision and Versatility
CNC laser cutting machines utilize a focused laser beam to cut, engrave, or mark various materials with unparalleled precision. The laser’s ability to produce fine, detailed cuts with minimal material wastage makes it a popular choice in industries that demand high accuracy and clean finishes.
Advantages:
- Minimal Material Wastage: Laser cutting is highly efficient, as the laser beam vaporizes the material along the cutting path, leaving behind a narrow kerf (cut width). This precision reduces material waste and allows for the creation of intricate designs that would be difficult or impossible with other cutting methods.
- High Accuracy: The precision of CNC laser cutters is unmatched, with the ability to cut materials to within fractions of a millimeter. This accuracy is particularly valuable in the production of components for industries like aerospace and electronics, where even minor deviations can result in product failure.
- Versatility: CNC laser cutters can work with a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, wood, and fabrics. This versatility allows manufacturers to use a single machine for multiple applications, reducing the need for additional equipment.
Applications:
CNC laser cutters are used in the aerospace industry to produce components with complex geometries and tight tolerances. They are also widely used in the electronics industry to create detailed circuit boards and in the signage industry to cut and engrave various materials for custom signs and displays.
Common Materials:
– Metals (e.g., steel, aluminum)
– Plastics (e.g., acrylic, polycarbonate)
– Wood (e.g., plywood, MDF)
– Fabrics (e.g., leather, textiles)

CNC Drilling Machines: Efficiency in Hole-Making
CNC drilling machines are designed to create precise, consistent holes in various materials. These machines are essential in manufacturing processes where multiple holes of the same size and depth are required, ensuring uniformity across all parts.
Key Operations:
- Drilling: Drilling is the most common operation performed by CNC drilling machines, where a rotating drill bit is used to create round holes in the workpiece. This operation is critical in the production of components that require fasteners, such as bolts or screws.
- Tapping: Tapping involves cutting internal threads in a hole, allowing for the insertion of screws or bolts. CNC drilling machines can perform tapping operations with high precision, ensuring that the threads are correctly aligned and sized.
- Reaming: Reaming is a finishing process used to slightly enlarge an existing hole, improving its surface finish and accuracy. This operation is often used in the production of high-precision components, such as engine cylinders and hydraulic parts.
Applications:
CNC drilling machines are widely used in the manufacturing industry to produce parts for machinery, vehicles, and electronic devices. They are also essential in the construction industry for drilling holes in structural components, such as beams and columns.
Common Materials:
– Metals (e.g., steel, aluminum)
– Wood
– Plastics
How to Choose the Right CNC Machine for Your Needs
Selecting the right CNC machine is crucial for achieving optimal results in your manufacturing process. The decision should be based on several factors, including the type of material you will be working with, the complexity of the parts you need to produce, the required production volume, and your budget. Below is an expanded comparison of the strengths and weaknesses of each machine type:
| Machine Type | Strengths | Weaknesses |
| CNC Milling Machines | Versatile, precise, suitable for complex shapes | Slower than some cutting methods |
| CNC Lathes | High precision for symmetrical objects | Limited to rotational parts |
| CNC Plasma Cutters | Fast, efficient for metal cutting | Limited to conductive materials |
| CNC Laser Cutters | Extremely precise, versatile | Higher operational costs |
| CNC Drilling Machines | Efficient in creating precise holes | Limited to drilling operations |
Industry-Specific Applications of CNC Machines
Each type of CNC machine has its niche within various industries, where their unique capabilities are leveraged to meet specific production needs:
- Automotive Industry
CNC machines are indispensable in the automotive industry, where they are used to produce critical components such as engine blocks, transmission parts, and body panels. The precision and repeatability of CNC machines ensure that every component meets strict quality standards, contributing to the safety and reliability of vehicles.
- Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry demands components with extremely tight tolerances and high levels of precision. CNC machines are used to manufacture parts such as turbine blades, aircraft frames, and landing gear components, where even the slightest deviation can have serious consequences.
- Electronics Industry
In the electronics industry, CNC machines are used to produce small, intricate components such as connectors, housings, and circuit boards. The ability to work with various materials, including metals and plastics, makes CNC machines versatile tools for electronics manufacturing.
- Medical Device Industry
Precision is paramount in the medical device industry, where CNC machines are used to produce components for devices such as implants, surgical instruments, and diagnostic equipment. The high level of accuracy ensures that these components meet stringent regulatory standards.
Future Trends in CNC Technology
As technology continues to evolve, the future of CNC machines looks promising, with several trends expected to shape the industry:
Automation and AI Integration: The integration of automation and artificial intelligence (AI) into CNC machines is expected to enhance efficiency and reduce human error. Automated CNC machines can operate continuously with minimal supervision, increasing production rates and reducing labor costs. AI algorithms can optimize machining processes by adjusting parameters in real time, improving accuracy and reducing material waste.
5-Axis CNC Machines: The use of 5-axis CNC machines is becoming more prevalent, allowing manufacturers to produce complex parts with fewer setups and greater precision. These machines can move the cutting tool along five different axes, making it possible to create intricate geometries and complex surfaces that would be difficult or impossible with traditional 3-axis machines.
Additive Manufacturing Integration: The combination of CNC machining and additive manufacturing (3D printing) is opening up new possibilities for producing hybrid components. By integrating both subtractive (CNC) and additive (3D printing) processes, manufacturers can create parts with complex internal structures, reducing weight while maintaining strength and functionality.
Sustainability and Green Manufacturing: As environmental concerns become more pressing, the CNC industry is focusing on sustainability. This includes the development of energy-efficient machines, the use of environmentally friendly materials, and the implementation of waste reduction strategies. Manufacturers are also exploring ways to recycle and repurpose scrap material, reducing the environmental impact of CNC machining.
Summary
Understanding the different types of CNC machines and their specific applications is crucial for anyone involved in modern manufacturing. Each machine type offers unique advantages and is suited to specific tasks, from producing complex geometries with CNC milling machines to achieving high-speed metal cutting with CNC plasma cutters. By choosing the right CNC machine, manufacturers can optimize their production processes, improve product quality, and stay competitive in a rapidly evolving industry. As CNC technology continues to advance, the potential for innovation in manufacturing is limitless, making it an exciting field for both seasoned professionals and newcomers alike.
FAQs
What are the six main types of CNC machines?
The six main types of CNC machines include milling machines, lathes, routers, plasma cutters, electric discharge machines (EDM), and laser cutters. Each machine type is tailored for specific applications, from creating detailed engravings to cutting through thick metal sheets.
What are the 6 major elements of a CNC machine?
The six major elements of a CNC machine are:
- Input Devices: These allow the operator to input data, such as designs or commands.
- Machine Control Unit (MCU): The brain of the CNC machine, processing instructions and controlling operations.
- Machine Tool: The component that performs the actual cutting, drilling, or shaping.
- Driving System: Powers the movement of the machine’s components.
- Feedback System: Monitors and adjusts the operations to ensure accuracy.
- Display Unit: Provides a visual interface for the operator to monitor the machine’s status.
How many types of CNC operations are there?
There are several types of CNC operations, including milling, drilling, turning, and laser cutting. Each operation involves different processes, tools, and setups to achieve the desired result on the workpiece.
What are the advantages of CNC machines?
CNC machines offer numerous advantages, including high precision, repeatability, efficiency in production, and the ability to produce complex parts with minimal human intervention. These machines are essential for modern manufacturing, where accuracy and speed are critical.










