In the modern manufacturing industry, the demand for precision machining is growing rapidly. Whether it’s mold manufacturing or high-precision part processing, the limitations of traditional cutting methods are becoming more evident. In this context, Wire EDM (Wire Electrical Discharge Machining) has emerged as an ideal solution for processing complex shapes and fine components, thanks to its non-contact and high-precision cutting features. Particularly in hard metal processing, complex contours, and micro-hole machining, Wire EDM offers unmatched advantages compared to other methods.
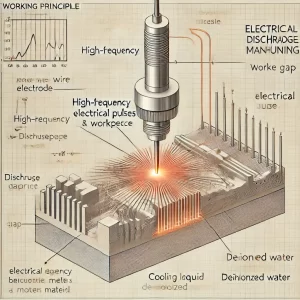
Wire EDM is a high-precision machining technology based on electrical discharge. It removes material through high-frequency discharges between a fine wire electrode and the workpiece, cutting out the desired shape. The main advantage of Wire EDM lies in its non-contact processing, which does not require applying mechanical force. This makes it suitable for machining materials that traditional cutting tools cannot handle. Additionally, Wire EDM is ideal for conductive materials and allows precise control of shapes and dimensions, enabling the creation of complex and fine geometries. Therefore, Wire EDM has become a key processing method in industries such as aerospace, medical, and mold making, where precision is critical.
In the following sections, this article will provide you with a comprehensive guide to Wire EDM, helping you make an informed decision when selecting a machining method.
What is Wire EDM?
Wire EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) is a technology that uses the principle of electrical sparks to perform high-precision machining on metals and other conductive materials. It works by using a fine metal wire as the electrode, generating high-frequency discharges between the wire and the workpiece to erode the material, thus achieving the cutting effect. Wire EDM is widely used in manufacturing, especially for precision machining, hard materials processing, and cutting complex geometric shapes.
How does Wire EDM work?
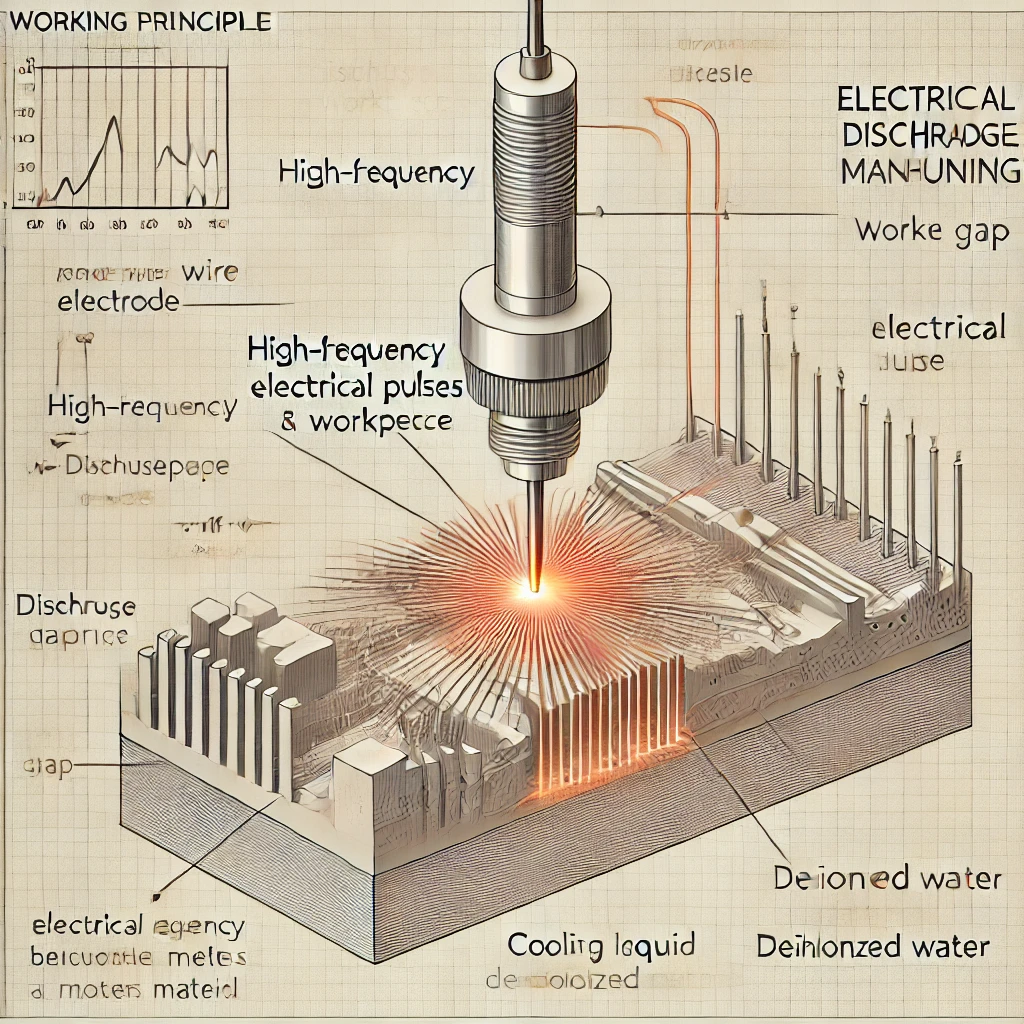
Wire EDM uses a fine metal wire, such as copper or molybdenum, as a moving electrode. During the machining process, a small discharge gap forms between the electrode wire and the workpiece. The high temperature generated by the discharge vaporizes and melts the material of the workpiece. This process takes place in deionized water or an insulating fluid, which cools the machining area and removes metal debris, ensuring stable and continuous cutting. The electrode wire is typically fed continuously to prevent wear, which helps maintain precision and achieve smooth, high-precision cuts.
Components of a Wire EDM Machine
A Wire EDM machine achieves high-precision cutting of workpieces through the close coordination of its various components. The precise control and collaboration of each part enable the machine to process complex-shaped parts within very tight tolerances. The key components include the following:
Electrode Wire Feeding System
The electrode wire (usually copper or molybdenum) is the cutting tool of the Wire EDM machine. The feeding system controls the speed and tension of the wire to ensure stability during the cutting process. The wire feeds continuously and is discarded after use, so the feeding and recovery system must be accurate to prevent wire breakage or misalignment.
Discharge Power Supply and Control System
The core of the Wire EDM machine is the pulse discharge system, which controls the discharge frequency, current, and voltage between the electrode wire and the workpiece. Through pulse discharges, the workpiece surface is eroded layer by layer. This system directly affects the machining efficiency and precision, as well as the surface roughness and cutting speed.
Worktable and Drive System
The worktable holds the workpiece and can move along the X and Y axes. The precision of the worktable’s movement is crucial for high-precision machining. The drive system, typically controlled by stepper motors or servo motors, ensures the workpiece is accurately positioned to meet the requirements of complex contours and multi-axis cutting.
CNC System (Computer Numerical Control)
The CNC system controls the movement paths of both the worktable and the electrode wire. Operators can program the CNC system to set cutting paths, feeding speeds, and discharge parameters. The CNC system is key to achieving automated machining and high-precision control, influencing the overall level of intelligence in the Wire EDM machine.
Cooling and Insulating Liquid System
Wire EDM machining is often performed in deionized water or oil-based insulating fluids. These fluids cool the machining area and prevent oxidation of the electrode wire and workpiece. The cooling system circulates the insulating liquid to remove heat and metal debris, ensuring cutting stability and cleanliness.
Wire Drum and Guide System
The wire drum stores the electrode wire, while the guide system directs the wire to the cutting area. The guide system ensures the precise positioning of the wire during high-frequency discharges to prevent misalignment, maintaining cutting precision. The guide system typically uses ceramic or hard materials to reduce wear and extend its lifespan.
Tension and Adjustment Device
The tension of the electrode wire is crucial for cutting quality and precision. The tensioning device adjusts and maintains a constant tension during cutting to prevent the wire from bending or breaking. This system ensures the stability of the wire during high-frequency discharges.
Waste Handling System
During cutting, a large amount of metal debris and waste liquid is produced between the electrode wire and the workpiece. The waste handling system filters and expels these small particles to prevent clogging in the cutting area. Additionally, the circulation and filtration of waste liquids are vital for maintaining machining precision.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Wire EDM
Wire EDM offers unique advantages in high-precision machining, complex shapes, and high-hardness materials, but its speed, energy consumption, and material costs limit its economic viability in mass production.
Advantages

- High Precision
Wire EDM can achieve micron-level precision, making it ideal for machining complex shapes, small tolerances, and high-precision parts. It is widely used in precision manufacturing fields such as mold making, aerospace, and medical devices. - No Mechanical Stress
Wire EDM removes material through electrical discharge, without applying direct mechanical cutting forces. This non-contact process is especially suitable for machining thin-walled workpieces, delicate parts, or hard, brittle materials, as it avoids workpiece deformation. - Suitable for Harder Materials
Wire EDM can machine harder conductive materials like tungsten carbide, titanium alloys, and stainless steel. This makes it one of the preferred methods for machining hard materials, especially in mold making. - Complex Shape Machining
The electrode wire can move along a preset path, enabling the cutting of free curves, complex profiles, and multi-axis movements. This makes it ideal for machining precision molds, gears, and screws. - High Surface Quality
Wire EDM can achieve low surface roughness in fine machining, often producing smooth surfaces that reduce the need for subsequent polishing or finishing work. - High Automation
The CNC system allows the Wire EDM machine to automatically control complex machining paths. The operation is simple and highly automated, making it suitable for batch production where consistency and efficiency are key.
Disadvantages
- Slow Machining Speed
Wire EDM removes material layer by layer, making it slower, especially for thick workpieces or fine details. It is not the optimal choice for large-scale cutting or situations where speed is critical. - Limited to Conductive Materials
Wire EDM relies on electrical discharge and can only be used for conductive materials, such as metals. It cannot process non-conductive materials, which limits its application in non-metallic material machining. - High Material Costs
The electrode wire is consumed continuously during the machining process and is usually discarded after one use. High-quality electrode wires, such as copper or molybdenum, are expensive. Additionally, the consumption of cooling liquids and insulating fluids adds to the production cost. - High Energy Consumption
Wire EDM requires continuous high-frequency discharges and relies on cooling and chip removal systems to maintain stable processing. This results in high energy consumption, making it less suitable for energy-efficient or environmentally-friendly machining needs. - Waste Liquid and Environmental Disposal Costs
Wire EDM generates waste liquids containing metal debris and conductive fluids, which must be properly handled. Environmental requirements are high, and disposal costs increase accordingly.
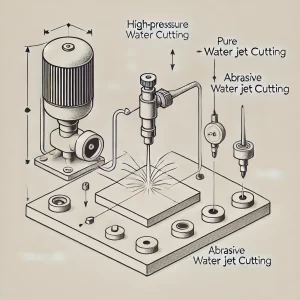
Differences Between Wire EDM and Water Jet Cutting
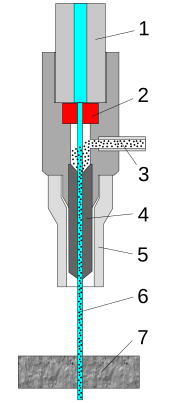
1.high-pressure water inlet
2.jewel (ruby or diamond)
3.abrasive (garnet) 4.mixing tube 5.guard
6.cutting water jet
7.cut material
Wire EDM and water jet cutting are both non-contact cutting technologies, but they differ significantly in working principles, materials, cutting precision, and application areas. Here are the detailed differences between the two:
Working Principle
- Wire EDM: Wire EDM uses the principle of electrical discharge. A fine wire electrode (usually made of copper, molybdenum, or zinc-coated wire) generates high-frequency discharges between the wire and the workpiece to remove material. The wire does not directly touch the workpiece; instead, the heat from the discharge vaporizes or melts the material, creating the cut.
- Water Jet Cutting: Water jet cutting uses high-pressure water to cut materials. The water pressure can reach thousands of bars. For cutting metals and hard materials, abrasive particles like garnet or quartz are added to the water stream, which increases the cutting ability. This is known as abrasive water jet cutting.
Applicable Materials
- Wire EDM: Wire EDM is suitable for conductive materials such as steel, copper, aluminum, titanium, stainless steel, and other metals. Due to the electrical discharge process, non-conductive materials like glass and ceramics are not suitable for wire EDM.
- Water Jet Cutting: Water jet cutting is suitable for almost all materials, including metals, plastics, ceramics, composites, glass, stone, rubber, and even food. Abrasive water jet cutting can effectively cut metals and hard materials, while pure water jet cutting is better for softer materials.
Cutting Thickness
- Wire EDM: Wire EDM can process thicker metal materials, typically ranging from 300 to 500 mm, with high-end machines capable of cutting even thicker materials. However, the cutting speed decreases significantly as the material thickness increases.
- Water Jet Cutting: Water jet cutting typically handles thicknesses up to 200 mm, although specialized water jet machines can cut thicker materials. Cutting thicker materials with water jets can affect precision to some extent.
Cutting Precision
- Wire EDM: Wire EDM generally offers high precision, typically achieving ±0.001 to ±0.005 mm. It is ideal for machining precision parts, especially in mold making and cutting complex shapes.
- Water Jet Cutting: Water jet cutting has relatively lower precision, usually around ±0.1 mm. However, high-precision water jet machines can achieve ±0.025 mm precision, but it still cannot match wire EDM in terms of precision for fine machining.
Speed
- Wire EDM: Wire EDM is slower, with cutting speeds typically ranging from 5 to 20 mm per minute. The speed depends on the required precision and material thickness.
- Water Jet Cutting: Water jet cutting is faster, especially with pure water jet cutting, which can reach cutting speeds of several hundred mm per minute. Abrasive water jet cutting for thicker materials slows down the speed but is still faster than wire EDM in most cases.
Surface Quality
- Wire EDM: Wire EDM typically produces smooth cuts, and with fine finishing, it achieves low surface roughness. This makes it suitable for parts that require a high-quality surface finish.
- Water Jet Cutting: The surface quality of water jet cuts is relatively rough, especially on thicker materials, with edges showing some burrs or ripples. Additional grinding or deburring processes are usually required to improve surface quality.
Thermal Effects
- Wire EDM: Wire EDM generates high temperatures, creating a heat-affected zone (HAZ) in the material, which can cause slight deformation or microcracks, especially in thin workpieces.
- Water Jet Cutting: Water jet cutting is a cold process with no heat-affected zone, making it ideal for materials that need to avoid thermal distortion, such as composites, rubber, and thin metals.
Application Areas
- Wire EDM: Wire EDM is widely used in precision mold making, aerospace, automotive parts, medical devices, and other fields. It is especially suitable for machining complex shapes and high-precision parts.
- Water Jet Cutting: Water jet cutting is used in various industries, including construction, stone processing, aerospace, automotive manufacturing, and food processing. Water jet cutting is particularly suitable for materials that are prone to thermal damage, such as composites, glass, and rubber.
Can Wire EDM Be Used for Drilling?
Yes! Wire EDM can be used for drilling, especially in applications that require precision and small hole machining. However, compared to traditional drilling methods, wire EDM drilling has specific use cases and limitations.
Features of Wire EDM Drilling
Suitable for Small and Irregular Holes
Wire EDM is excellent for machining small diameter holes and complex-shaped holes. It can create holes of any geometry, such as square, oval, or other irregular shapes, which are difficult to achieve with traditional drilling methods.
Non-contact Processing
Wire EDM is a non-contact process that does not apply mechanical force to the material. This makes it ideal for drilling brittle materials, such as carbide, ceramics, and thin-walled materials, avoiding cracking or deformation caused by mechanical stress.
High Precision
Wire EDM drilling provides extremely high precision, with accuracy typically up to ±0.01 mm or better. This is perfect for applications where hole size precision is critical.
Suitable for Conductive Materials
Wire EDM can only be used to drill conductive materials, such as metals and some conductive alloys. Non-conductive materials like glass or plastics cannot be drilled with wire EDM.
Limitations of Wire EDM Drilling
Starting Hole Requirement
Wire EDM requires a starting hole for the electrode wire to pass through in order to begin the cutting process. This means a hole must be pre-drilled before the wire EDM process can start, which makes it different from direct drilling methods.
Slower Processing Speed
Wire EDM drilling is relatively slow, especially when working with thicker materials. As the material thickness increases, the speed of drilling decreases. Therefore, wire EDM is not ideal for high-speed drilling or large-volume production of standard holes.
Equipment Cost and Consumables
Wire EDM machines and operation costs are higher compared to traditional drilling. The process also consumes electrode wires and cooling fluids, making it less cost-effective for high-volume drilling or simple hole machining.
Typical Applications
- Mold Manufacturing: Wire EDM is often used for high-precision small holes or complex-shaped holes in molds, such as guide holes in stamping dies.
- Precision Mechanical Parts: It is suitable for industries like aerospace and medical equipment, where hole shape and precision are critical.
- Hard Materials: Wire EDM can drill holes in hard materials, such as carbide, avoiding mechanical stress, making it ideal for drilling in hard-to-machine materials.
Why Is Wire EDM Processing Expensive?
Wire EDM processing is costly due to multiple factors, including equipment, materials, consumables, technical requirements, and energy consumption. As a result, wire EDM is typically used for specific applications that require extremely high precision, complex shapes, or hard materials, ensuring high-quality results.
The main reasons for the high cost of wire EDM processing include the following:
1. High Equipment and Maintenance Costs
Wire EDM machines are precision CNC equipment with complex structures and high costs. Their core components, such as the servo system, high-frequency discharge system, and control system, require precise calibration. To maintain the machine’s accuracy and lifespan, regular maintenance is necessary, including replacing electrode wires, cleaning the cooling system, and changing the insulating liquid.
2. Slow Processing Speed
Wire EDM removes material layer by layer through electrical discharge, which is slower than traditional cutting methods. This is especially true for fine machining or cutting thick materials, which increases the processing time. Longer processing times result in higher costs for each part.
3. High Electrode Wire Consumption
Wire EDM uses electrode wires (such as copper or molybdenum) that are continuously fed into the machine, causing them to wear out during processing. High-quality electrode wires are expensive, and the consumption rate is higher during precision machining. As a result, material consumption directly contributes to the higher cost of wire EDM processing.
4. High Cost of Insulating Liquid and Disposal
Wire EDM uses insulating liquids, such as deionized water, which need to be replaced regularly to maintain stable processing. These liquids also need to be filtered periodically to remove metal debris and impurities, increasing production costs. Additionally, the disposal of waste liquids requires careful environmental handling, which further adds to the cost.
5. High Skill Requirements for Technicians
Wire EDM requires high precision, so skilled technicians are needed to operate and program the machine. The salaries of these technicians are relatively high, and this labor cost is reflected in the processing fees. Additionally, the time required for machine setup, debugging, and programming increases the cost for each part.
6. Narrow Application Range
Wire EDM is limited to conductive materials and is mainly used for high-precision machining and cutting complex shapes. The demand for wire EDM is concentrated in high-end manufacturing fields, such as precision molds and aerospace components, where production volumes are low. This smaller market size results in higher unit processing costs.
7. High Energy Consumption
Wire EDM relies on continuous pulse discharges during processing, which requires stable high-frequency discharges and cooling systems. This results in significant energy consumption, leading to higher electricity costs. The high energy consumption further increases the overall processing cost.
Conclusion
In conclusion, wire EDM technology has become a key technique in modern precision manufacturing due to its exceptional accuracy, non-contact processing, and adaptability to complex shapes. This article has introduced the working principles, application scope, advantages, and limitations of wire EDM, helping you gain a clearer understanding of its practical applications. When it comes to meeting high standards and strict processing requirements, selecting the right wire EDM machine is crucial.